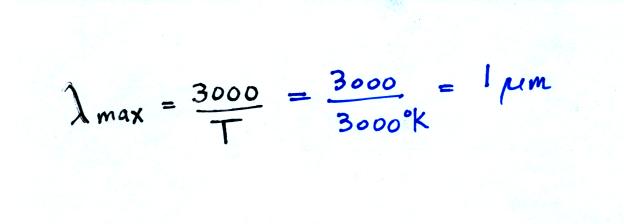Optional Assignment #3
Answers
1.
Is Point A in the figure
below in
a RIDGE or a TROUGH?
Would the winds at Point B blow toward
the
NORTHEAST SOUTHEAST
SOUTHWEST or NORTHWEST?
Would you expect to
find relatively WARM
or COLD air below Point C?
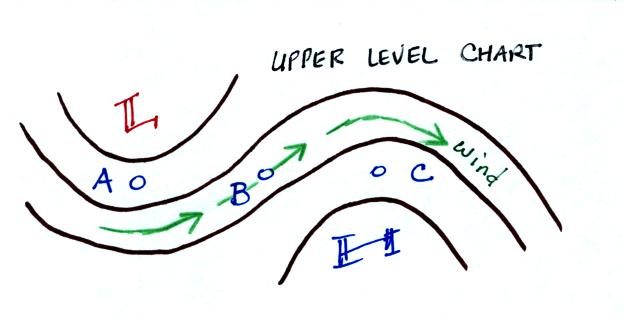
The winds on upper level charts
blow parallel to the contour lines from west toward east.
2.
Based on the directions and
amounts of air movement at the surface and at upper levels, would you
expect the surface pressure to INCREASE, remain the
SAME, or
DECREASE?
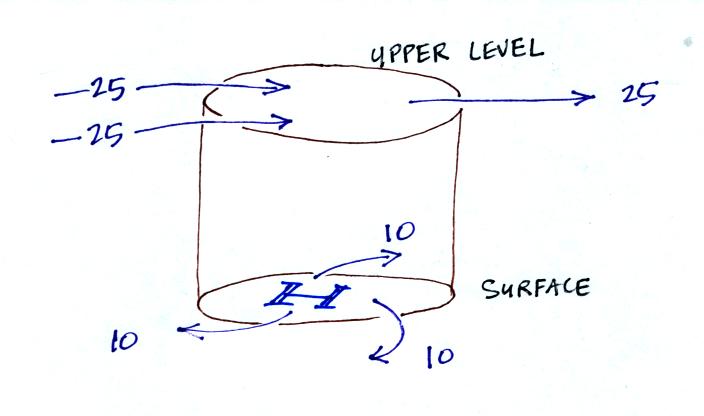
There's a total of 25 + 25 =
50 units of air being added to the cylinder (all occurring at upper
levels). There are 25 units of air being removed at upper levels
and 3 x 10 = 30 units being removed at the surface. That is a
grand total of 55 units. There are 5 more units being removed
than being added. So the weight of the cylinder will
decrease. Since the surface pressure is determined by the weight
of the air in the cylinder the surface pressure will also
decrease. Want some more practice? Here is a link with more examples.
3.
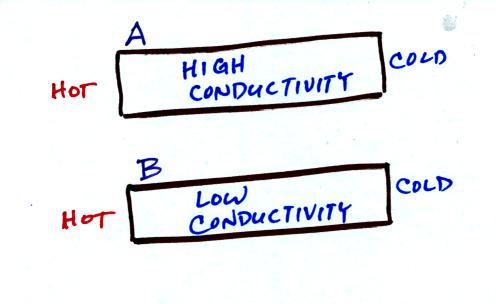
The rate at which energy is
transported through an object by conduction depends on the thermal
conductivity of the material and on the temperature gradient. Do
you
think energy would be transported more rapidly through
OBJECT A or
OBJECT B in the figure below? (A has high thermal
conductivity, B has
low conductivity; the temperature gradients are the same)
Do you think energy would be
transported more rapidly through OBJECT C or OBJECT
D below. (Both
materials have the same thermal conductivities, the temperature
gradients are different)
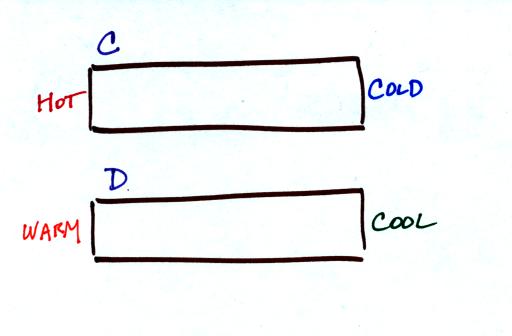
What if there were no temperature
difference or no temperature gradient. In that case there
wouldn't be any energy flow.
An analogous situation might be tripping and rolling down a
slope. You wouldn't roll very fast down a gradual slope.
You would roll much more quickly on a steep slope.
4.
A cold southward flowing
ocean current (the California current) is
found on the west coast of the United States, a warm northward current
(the Gulf Stream) is found off the east coast. Both currents
transport
energy from the tropics to the polar regions. Oceans currents
like
these illustrate energy transport by
a.
conduction
b.
convection
c. electromagnetic
radiation
d. latent heat
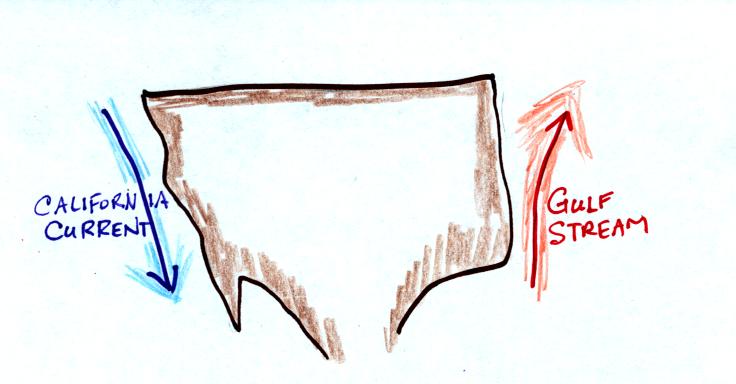
Many people would probably choose
latent heat because water is involved. But in order for latent
heat energy transport to occur there must be changes in phase.
There is no mention of evaporating water or freezing water in this
problem.
Oceans currents are organized motions (of water molecules)
however. Organized motions of atoms or molecules in a gas or a
liquid is convection.
Some people might worry about how a cold current transports
energy. When cold water moves leaves Location A and heads
to Location B it makes room for warm water (from somewhere else)
to move into Location A. That is how energy is being transported.
5.
Would a positive charge
placed at the x in the figure below, exactly half way
between the + and - charges, move to the
RIGHT, move to
the LEFT, or NOT
MOVE at all?

A positive charge placed at X
would be repelled by the +
charge at left and attracted to the -
charge at right.
6.
Are Points A and B in the
figure below exactly 1/4
1/2 3/4 or 1
wavelength apart?
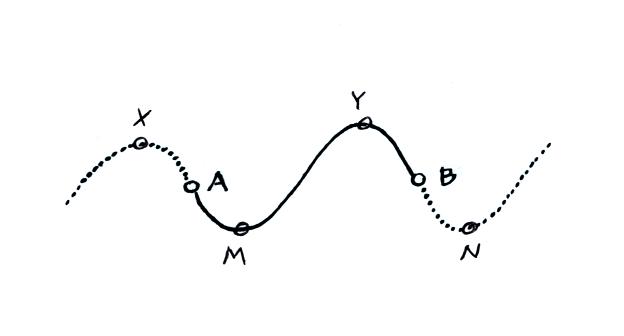
You need to find identical points
on the wavy pattern. Points X and Y are also 1 wavelength
apart,
so are M and N.
7.
What was Isaac Newton able to
demonstrate by shining white light
through a glass prism?
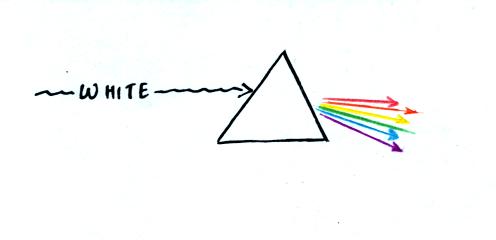
Newton found that the white light
was split into colors. Newton demonstrated that what we perceive
as white light is a mixture of
colors. You'll find a picture of this experiment in
Fig.15.20 on p. 415 in the text.
8.
Is
UV-A
UV-B or UV-C the
most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation?
Does VISIBLE
light
MICROWAVE radiation
or INFRARED light
have the shortest wavelength?
UV-C has wavelengths 0.2 to 0.29 micrometers, UV-B 0.29 to 0.32
micrometers, and UV-A 0.32 to 0.4 micrometers. The shorter the
wavelength, the more energetic the radiation. Figure 2.6 on p. 32
gives typical wavelengths of visible (5 x 10-7 meters or 0.5
micrometers), IR light (10-6 meters or 1 micrometer) and
microwave
radiation (10-3 meters or 1000 micrometers)
9.
Which of the following is not
a form of electromagnetic radiation?
a. gamma
rays b. radio
waves c. sound
waves d.
x-rays
10.
Does filter absorption
CURVE A or
CURVE B correctly depict the behavior of
the red filter shown below at left?
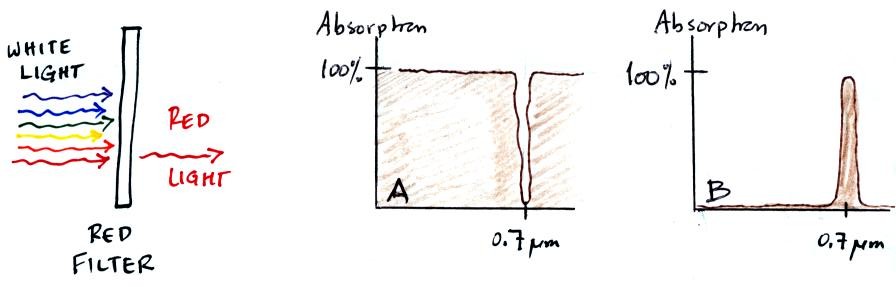
A red filter will absorb all
colors except for red. The filter transmits red light.
Curve A shows 0% absorption of 0.7 micrometer light (red light) and
100% absorption of all the other colors.
11.
The temperature of the
tungsten filament in a bulb is about 3000 K. What is the
wavelength of peak emission? What kind of light is that, can you
see it?
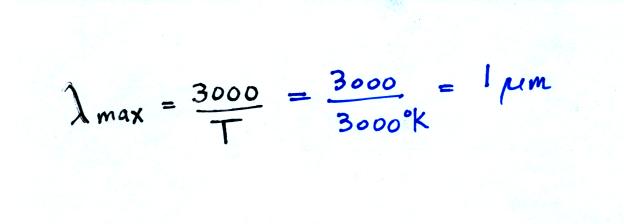
We used Wien's Law to calculate
lambda max. This is near
infrared radiation, it is invisible (at least for people, there
may be some animals, or reptiles or insects that can see this kind of
light).
12.
About half (49%) of the light
emitted by the sun is UV
VIS IR
light.
44% of sunlight is visible light, the remaining 7% is ultraviolet light.
13.
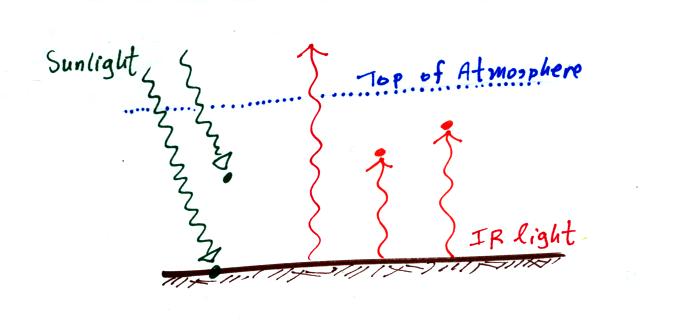
How many total units of
energy is being absorbed by the atmosphere? The atmosphere is absorbing 3 units (1
unit of sunlight and 2 units of IR radiation emitted by the earth).
How many units of
energy is being absorbed by the ground? 1 unit of sunlight makes it through the
atmosphere and is absorbed by the ground.
How many units of energy
must the atmosphere emit to be in radiative equilibrium? Because it is absorbing 3 units, it
must also emit three units.
How many
units of energy must the ground receive from the atmosphere to be in
radiative equilibrium? The
ground needs 2 more units of radiation to be in balance.
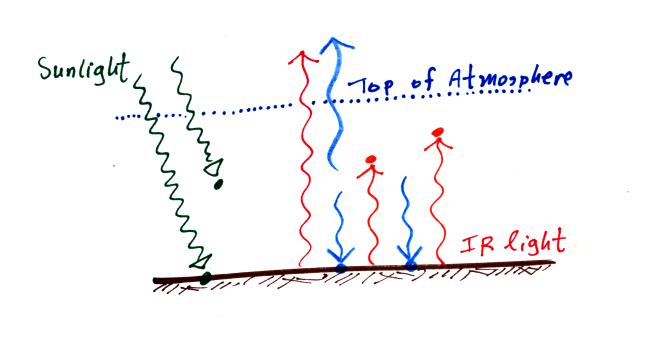
The 3 units of energy emitted by
the atmosphere are shown in this figure. 2 units are sent
downward to the ground to achieve energy balance there. The third
unit is sent up into space.
14.
There is an atmospheric
greenhouse effect on the earth because
a. oxygen and ozone absorb UV light
b. condensation of water vapor releases energy into the air
c. carbon dioxide and water
vapor (and all the other greenhouse gases) absorb IR light
d. water has a higher specific heat than soil
All of the statements are
accurate. However only c is part of the atmospheric greenhouse
effect.
15.
Based on the information
given (neither figure is in radiative equilibrium) would the
temperature of the ground in Figure A below be WARMER
COLDER or the SAME
as the ground in Figure B?
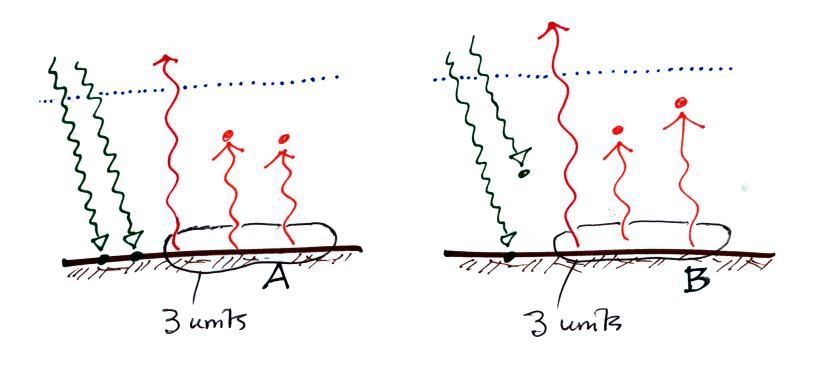
The important detail is that the ground is emitting the same amount of
energy in both cases. This is another of those Stefan-Boltzmann
law ( "the rate at which an object emits energy depends on the object's
temperature (to the 4th power)" ) questions. The ground
temperature must be the same in both figures for the ground to be
emitting energy at the same rate.