
1. Identify the cloud in the picture
a. altocumulus
b. cirrus
c.
nimbostratus
d. cumulonimbus
2. Which of the following is NOT a way that fogs form?
a. Increase surface air temperature
b. Decrease surface air temperature
c. Increase water vapor in the air
3. Which is the type of fog that occurs when cold air flows over much warmer water.
a. Radiation b. Steam c. Upslope d. Advection
4. Which of the following is NOT true about Dry adiabatic conditions
a. are associated with rapid decompression
b. apply when rapidly lifting a parcel of air upward through the atmosphere
c. apply in clear conditions when there
is condensation
d. are associated with compression when the parcel sinks rapidly to lower altitudes
5. Circle the letter of the numerical value on the right corresponding to the description on the left (NOTE: 2 have identical values).
I. Temperature decrease with height under MAR conditions A. -10oC/km
II. Temperature decrease with height under DAR conditions B. -8oC/km
III. Dew point decrease with height under DAR conditions C. -6oC/km
IV. Dew point decrease with height under MAR conditions D. -2oC/km
(Remember inside a cloud where relative humidity is 100%, the dew point temperature equals the air temperature)
I.
C.
II.
A.
III.
D
IV.
C.
6. Why do the moist and dry adiabatic rates differ?
a. The rising motion associated with moist adiabatic is slower
b. Moist adiabatic occurs in clouds where there is less sunlight and solar heating
c.
One includes the effect of
latent heat release, the other does not

7. If the temperature of the surface air on the west (left) side of the mountain stayed the same but the dew point of that air decreased, the height of the base of the cloud would
a. increase b. decrease c. stay the same
8. What is the approximate relative humidity of the air at 1 km altitude on the EAST side of the mountain?
a. 5% b. 20% c. 33% d. 60%
9. Which of the following is NOT a reason the relative humidity of the surface air on the east side of the mountain is so low (where the deserts are in California, Oregon and Washington)?
a. The amount of water in the air has been reduced because some of the water in the air rained out on the mountain as it rose up and over the mountain
b. The temperature of the surface air on the east side is higher because air temperature increases more as it sinks (and compresses) on the east side (following the DAR) than it cooled on the way up on the west side
c.
The higher temperatures on the
east side cause lower saturation vapor pressures which reduce the relative
humidity
d. Winds tends to be westerly at the middle latitudes of CA, OR and WA
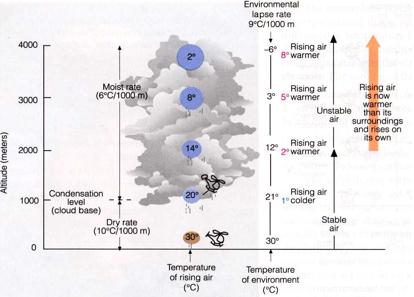
SIMILAR to the figure above, suppose the environmental lapse rate (ELR) were 7.5oC/km with a surface temperature of 25oC and surface dew point of 17oC.
10. Fill out the table below to help with questions 12-15
|
Altitude (m) |
Environmental Air Temp (oC) |
DAR or MAR |
Temperature of rising air parcel (oC) |
Dew point of rising air parcel (oC) |
Rising air parcel temperature relative to
environment: same, warmer, or cooler |
Clear or cloudy |
|
3000 |
2.5 |
MAR |
3 |
3 |
warmer |
cloudy |
|
2000 |
10 |
MAR |
9 |
9 |
cooler |
cloudy |
|
1000 |
17.5 |
MAR |
15 |
15 |
cooler |
cloudy |
|
0 |
25 |
DAR |
25 |
17 |
same |
clear |
11. What is the approximate relative humidity of the rising air parcel at 2 km alitude?
a. 25% b. 60% c. 90% d. 100%
12. At what level will a cloud form when surface air is lifted?
a. 1000 m b. 2000 m c. 3000 m
13. What temperature lapse rate do you use to describe how the temperature changes with altitude within the cloud?
a. DAR b. MAR c. ELR
14. At approximately what altitude will the air lifted from the surface become warmer and therefore lighter than the surrounding environmental air and start rising by itself?
a. 1000m b. 2000 m c. 3000 m
15. Which of the following is NOT a reason why forecasters are concerned with stability and lapse rates?
a. determining altitude of cloud base
b. determining altitude of positive buoyancy of lifted air
c. the wind chill factor
d. speed of updrafts
e. The probability and size of hail
16. When we say conditionally unstable, what condition is necessary to bring on the instability
a. high surface temperatures b. conduction c. sunlight d. condensation
17.
 For the stability of the atmosphere to change, the
For the stability of the atmosphere to change, the
a. ELR must change
b. DAR must change
c. MAR must change
(NOTE: only one of these 3 is
changeable!)
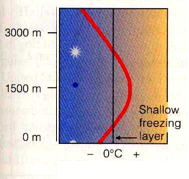
18. Which type of precipitation is associated with the conditions in the figure to the right?
a. Sleet
b. Snow
c. Rain
d. Freezing rain
19. Which of the following is NOT true about Freezing Rain
a. Causes beautiful icicles
b. Occurs when supercooled water droplets hit the surface which is below freezing
c. Is a form of hail
d. Causes power lines to break
e. Causes automobile accidents
20. Circle the letter of the size on the right corresponding to the object on the left. (Now aligned)
I. The typical size of a rain drop A. 2 mm
II. The typical size of a cloud condensation nucleus B. 0.2 microns
III. The typical size of a cloud droplet C. 20 microns
21. Why does air pressure decrease more quickly with increasing altitude when the air is cold
a. gravity is weaker in cold air
b. the air is more compressed or dense when cold
c. air is more expanded when cold
22. An Isobar is a contour of constant
a. wind speed b. density c. temperature d. pressure
23. If the measured surface pressure at Flagstaff is 795 mb, what is the Flagstaff surface pressure converted to sea level? (Flagstaff is 2134 m above sea level)
a. 928 mb b. 998 mb c. 1008 mb d. 1018 mb
24. If the measured surface pressure at Phoenix is 966 mb, what is the Phoenix’s surface pressure converted to sea level? (Phoenix is 337 m above sea level)
a. 928 mb b. 990 mb c. 1000 mb d. 1303 mb
25. Given the two previous sea level pressures, which direction is the PGF pointing?
a. north b. south c. east d. west
26. Surface pressures are converted to equivalent pressure at sea level for understanding the forces driving the winds. Why?
a. horizontal temperature gradients are much larger than vertical temperature gradients
b. horizontal pressure gradients are much larger than vertical pressure gradients
c.
vertical pressure gradients are
much larger than horizontal pressure gradients
Extra
Credit
27. Explain how the demonstration in class showed that cloud concentration nuclei (CCN) are important in forming clouds.
28. Where was the highest surface pressure ever measured? Approximately what was that pressure? Make sure you show the units. Was it during summer or winter? Explain why. Was it over land or over water? Explain why.
29. Under what meteorological conditions was the lowest surface pressure ever measured? Approximately what was that pressure? Make sure you show the units. Was it during summer or winter? Explain why. Was it over land or over water? Explain why.
30. Describe how the process of collision and coalescence produces rain.
Answer Sheet
1. a b c d e
2. a b c d e
3. a b c d e
4. a b c d e
5.
I. a b c d
II. a b c d
III. a b c d
IV. a b c d
6. a b c d e
7. a b c d e
8. a b c d e
9. a b c d e
10. Fill out table
11. a b c d e
12. a b c d e
13. a b c d e
14. a b c d e
15. a b c d e
16. a b c d e
17. a b c d e
18. a b c d e
19. a b c d e
20.
I. a b c
II. a b c
III. a b c
21. a b c d e
22. a b c d e
23. a b c d e
24. a b c d e
25. a b c d e
26. a b c d e