Optional Assignment #1
Answers

If you doubled N and T, P would increase by a factor of 4. But
then when you double V, the pressure is divided in half. So the
net result of doubling N, T, and V is to increase the pressure by a
factor of 2.

The important thing to remember is that a mercury barometer is a
balance. The balance part of the barometer is colored red
above. On the left a tall column of air (light brown) is balanced
by a much shorter column of mercury (green). No air is able to
get into the top of the right tube of the barometer. So there is
not any pressure pushing on the top of the mercury column.

It is not necessary, but if you were to decode all of the plotted
pressure data you would see that the pressure values get smaller
as you move into the center of the pattern. This is a center of
low pressure. Surface winds spin counterclockwise and spiral
inward into centers of low pressure in the northern hemisphere.


Cold fronts are normally drawn blue, warm fronts are red. An
occluded front is usually colored purple. A stationary front has
alternating blue and red segments and the triangles and half circles
point in opposite directions.

Pressure changes at a rate of 1 mb per 10 meters of altitude change.
In A: Multiply 500 m by the 1 mb/10 m rate of change. You
get a total change of 50 mb. Thus the station pressure is 1003.7
mb - 50 mb = 953.7 mb. You must subtract the correction because
pressure decreases with increasing altitude.
In B: Multiply 750 m by 1 mb/10 m and you get 75 mb. You must add
this correction to the measured station pressure. 935.1 mb + 75
mb = 1010.1 mb.
In C: First subtract 915.9 mb from 1005.9 mb. You get a total change of
90 mb. Next you diivide this by the 1 mb/10 m rate of change of
pressure. You get 900 meters.
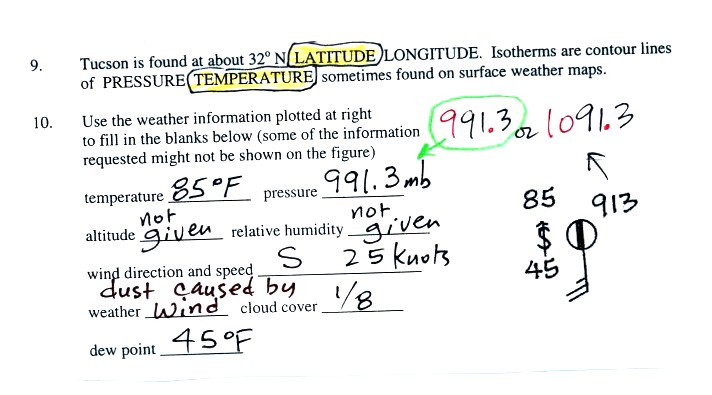
The altitude and the relative humidity are not given. If the dew
point and the air temperature were the same you could say the relative
humidity was 100%.

The effects of upper level and surface divergence and convergence are
shown below
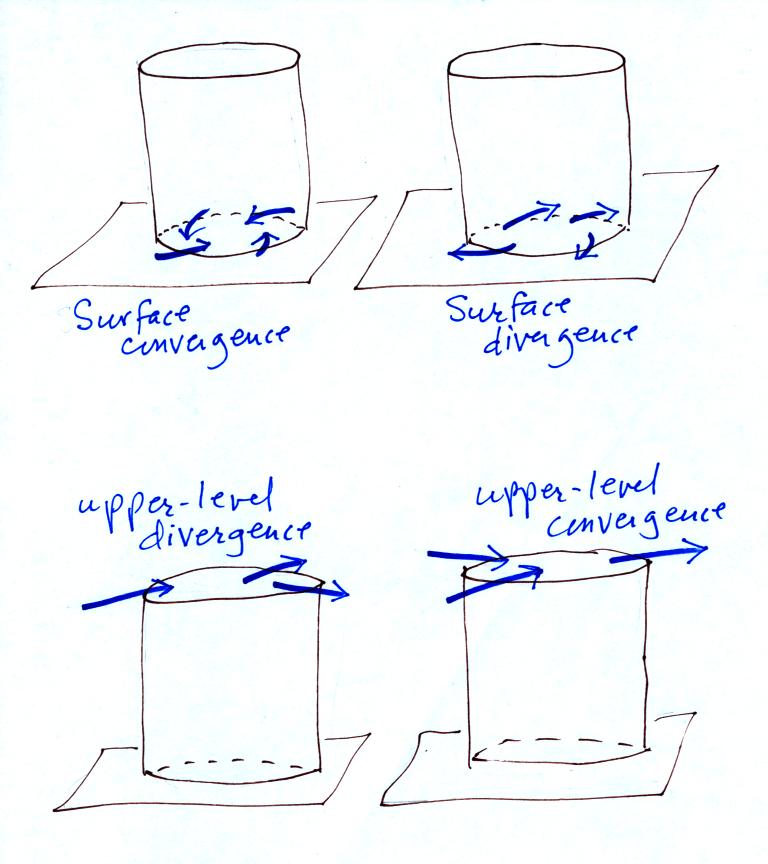
Convergence (either at the surface or aloft) will add air to the
cylinder. The cylinder will weigh more and since sea level
pressure is determined by the weight of the air overhead, the surface
pressure will increase.
Surface or upper level divergence will cause the surface pressure
to decrease.










