On the previous page, it was shown that the official Atlantic Hurricane season lasts from June first through the end of November, and that on average, there are 10.6 tropical storms, 5.9 hurricanes, and 2.0 major hurricanes (category 3 and higher). Figure 8 shows that Atlantic hurricane activity peaks in early September and that storms occasionally form outside the official hurricane season in May and December. This pattern of hurricane occurrence is closely correlated with the seasonal change in Atlantic sea surface temperature. The highest sea surface temperatures in the Atlantic typically occur in early September.
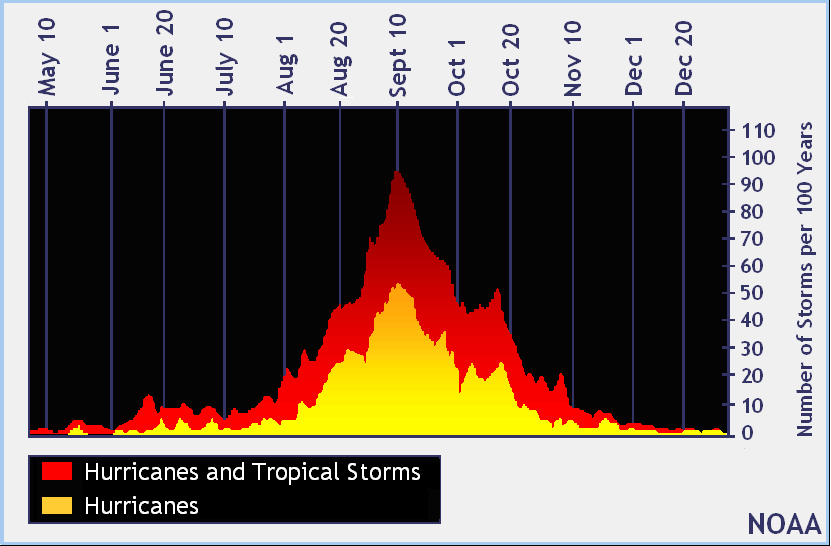 |
| Figure 8: Average number of Atlantic Hurricanes per century as a function of calendar date. |
In addition, there is quite a bit of variation in the number of Atlantic hurricanes from year to year as shown in figure 9.
 |
| Figure 9: The number of hurricanes in the Atlantic basin each year from 1944 to 2007 (the caption above the figure is incorrect). Red indicates the number of major hurricanes (category 3 and higher), while blue indicates all hurricanes. In 2008, there were 8 Atlantic hurricanes, 5 of which were major hurricanes. |
An obvious question comes to mind: "Is there a significant temporal pattern in the number of Atlantic hurricanes?" Many researchers have concluded that there is a multi-decadal cycle, consisting of 20 - 40 year periods of increased hurricane activity followed by 20 - 40 year periods of decreased hurricane activity. Although a bit difficult to see, this cycle can be seen in figure 9 above. There appears to have been more and stronger hurricanes from 1944 through the mid to late 1960s, then fewer and less powerful hurricanes from about 1970 through the mid 1990s, then higher numbers of hurricanes again from 1995 through 2006.
Another piece of evidence is shown in figure 12 below. The figure presents a metric called Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE). ACE measures the total wind energy realized over the entire life cycle of all storms in a tropical season. ACE factors in storm intensity, frequency, and duration. Put simply, a long-lived very powerful Category 3 hurricane may have more than 100 times the ACE of a weaker tropical storm that lasts for less than a day. As the annual ACE index grows, it indicates that the total wind energy generated by tropical cyclones that year had a great deal of damaging potential. We see generally high damage potential during the period from 1950 to 1969, followed by generally low damage potential from 1970 to 1994, then generally high after 1995. In particular the 2004 and 2005 seasons stand out. Most researchers believe that these trends are significant. The reason for the trend seems to be related to natural fluctuations in the Atlantic sea surface temperature and wind patterns. During active periods, sea surface temperatures are high and wind patterns favor storm development. Based on this information, we should expect hurricane activity in the Atlantic basin to remain high for at least the next 5-10 years.
 |
| Figure 12: Seasonal Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) index for the North Atlantic Ocean basin from 1949 - 2008. |
While variations in the total number of hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean is interesting, keep in mind that most people only remember the ones that cause death and destruction on the coast. Many Atlantic hurricanes stay out at sea or are relatively weak when they make landfall. Those few hurricanes that reach category 4 and 5, only remain at that strength for short periods of time, which on average is less than 24 hours. The chance that one of these monsters will hit the U.S. mainland as a category 4 or 5 storm is relatively low (see Table 4, which lists the 60 most intense hurricanes at the time of landfall in the United States from 1851-2004). Note that from 1851-2004 there were only 3 category 5 and only 15 category 4 hurricanes at the time of landfall with the continental United States. During the 2005 hurricane season, Katrina hit as a category 4 storm and Dennis, Rita, and Wilma hit land as a category 3 storms. The fact that major hurricanes hit the mainland U.S. so infrequently contributes to public unawareness of their potential devastion (see last section below). In particular very few powerful hurricanes struck the U.S. mainland from 1970 - 1990; People from that era became desensitized to the potential devastion of hurricanes and developed a false sense of security.
Map indicating the location and strength of all major landfalling hurricanes (category 3 and higher) in the United States from 1899 through 2007. The overall average is slightly less than one per year. 2005 had a record of four major landfalling hurricanes: Dennis, Katrina, Rita, and Wilma.
Public attention for hurricanes is primarily driven by lanfalling hurricanes that result in death and destruction, rather than fluctuations in the number of hurricanes in the Atlantic. In 2004, four hurricanes (three major hurricanes) hit the state of Florida, followed in 2005 by Katrina, the most costly natural disaster in United States history, as well as three other major landfalling hurricanes, Dennis, Rita, and Wilma. In fact, the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was record-breaking. The 27 named tropical storms broke the old record of 21; 15 of these tropical storms became hurricanes, breaking the old record of 12; 4 hurricanes made landfall over the United States at category 3 or higher breaking the old record of 3 set in 2004. A good summary of the record breaking hurricane season of 2005 is given in the article: 2005: A Hurricane season 'On Edge'. The result is that hurricanes are under public scrutiny. And anytime a weather disaster happens today, you can be sure that someone will try to link it to global warming.
The basis for a link to global warming is as follows ... As humans add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, the average surface temperature of the Earth should increase. Exactly how much and how fast it may warm is a matter for debate. One consequence is that global sea surface temperatures will increase. Measurements do show that the global average sea surface temperature has been increasing in recent years ... Therefore, since hurricanes feed off warm ocean water, the recent strong landfalling hurricanes in the United States directly results from global warming.
While the above argument seems plausible, it cannot be scientifically proven at this time. As mentioned above, the recent increase in Atlantic hurricanes can be better explained as a continuation of the multi-decadal cycle discussed above. The 2004 and 2005 hurricane seasons are not overly abnormal when viewed in the context of hurricane cycles over the last 100 years and beyond. The multi-decadal cycle itself certainly cannot be attributed to global warming. Furthermore, hurricane development requires more than just warm sea surface temperatures -- how are these other development factors influenced by global warming? While we cannot say with certainty that global warming has had no influence on hurricane development, based on the best available scientific evidence, it is wrong to say that global warming has been directly responsible for the 2004 and 2005 hurricanes (also see statement from Dr. William Gray at the end of this section). I believe it is dangerous to explain Katrina (or even the record-breaking 2005 hurricane season) through global warming because we have always had strong hurricanes in the USA - the strongest one on record dates back to 1935.
On the other side of the issue, a 2005 study by Kerry Emanuel, a leading U.S. hurricane researcher, has concluded that while the number of hurricanes have not changed, the windspeeds (a measure of storm intensity) have increased in recent years. However, it has not been scientifically proven that the increased hurricane windspeed is defintely due to global warming. One problem with that study is that we can only look back about 35 years with satellite data; before that the hurricane record is somewhat unreliable, and 35 years isn't long enough to draw a definite conclusion. We certainly can't rule out the possibility that this is part of a natural cycle in hurricane activity. Before global satellite coverage, there are gaps in the historical hurricane record; thus, prior to 35 years ago, even strong storms that spent their entire lifecycle out at sea, were probably unnoticed. We are going to need many more years of good hurricane observations before we will be able to conclude without doubt that global warming is having a large impact on the intensity of hurricanes ... to be able to rule out the possibility that observed fluctuations in hurricane intensity are not part of a natural climatic cycle.
In fact, in a more recent study published in 2008, Emanuel says he will now reconsider his strong assertation of a link between global warming and more intense hurricanes (see Hurricane expert reconsiders global warming's impact). He does not rule out a link, but the new study indicates that in a warmer world stronger wind shear may actually reduce hurricane activity. While Emanuel is an honest scientist, basing his statements on the latest scientific studies, the news media is much more likely to report on a possible negative impact of global warming, rather than presenting an honest evaluation of all current scientific evidence and uncertainty. The debate concerning this issue will continue ... see for example Hurricanes Have Doubled Due to Global Warming, Study Says dated July 30, 2007 and Warmer Ocean Could Reduce Number of Atlantic Hurricane Landfalls dated January 22, 2008, as examples.
Perhaps the most damaging evidence against a direct link between global warming and hurricane intensity is based on the fact that worldwide (global) ACE values are currently near 30 year lows in spite of warmer ocean waters (see Great Depression! Tropical Cyclone Energy at 30-year lows). You should look at the figure at the top of the linked page and read over the last section "Bottom Line." This was also pointed out in a recent USA Today artical Tropical cyclone activity at 30-year low in N. Hemisphere). The figure below for Northern Hemisphere ACE through 2008 shows the same thing.
 |
| Figure 13: Seasonal Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) index for Northern Hemisphere Hurricanes 1950 - 2008. |
What does this figure tell us about a possible link between global warming and hurricane intensity? It shows that there is no obvious trend (just eyeballing the data) with time in yearly hurricane energy in the Northern Hemisphere as measured by ACE. The fact that the most recent years had low activity indicates that the simple predictions by some global warming alarmists, which predicted stronger and more frequent hurricanes following the devastating storms of 2004 and 2005, have not happened. However, the figure does not rule out a link between global warming and more intense hurricanes either. I believe that we can probably say something like this: The impact of global warming on hurricane activity (if there is an impact) in today's climate is probably small compared to the modulation of hurricane strength by natural climate factors, i.e., since 1950 the natural variations are much larger than any long-term trend that may be due to global warming.
In spite of the lack of scientific proof, many in the media flock to those who make assertations about influence of global warming on United States hurricanes. See Germany's Environment Minister, Juergen Trittin, cites greenhouse gas emissions as cause for Katrina. In my opinion, the German minister (among others) is using the Katrina disaster to further his agenda to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases for fear of global climate change. While this is a noble agenda, he should base his arguments on sound scientific evidence, not scare tactics.
The following statement was taken from FORECAST OF ATLANTIC HURRICANE ACTIVITY FOR SEPTEMBER AND OCTOBER 2005 AND SEASONAL UPDATE THROUGH AUGUST by William Gray and Philip Klotzbach:
"Many individuals have queried whether the unprecedented landfall of four destructive hurricanes in a seven-week period during August-September 2004 and the landfall of two more major hurricanes in the early part of the 2005 season is related in any way to human-induced climate changes. There is no evidence that this is the case. If global warming were the cause of the increase in United States hurricane landfalls in 2004 and 2005 and the overall increase in Atlantic basin major hurricane activity of the past eleven years (1995-2005), one would expect to see an increase in tropical cyclone activity in the other storm basins as well (ie., West Pacific, East Pacific, Indian Ocean, etc.). This has not occurred. When tropical cyclones worldwide are summed, there has actually been a slight decrease since 1995. In addition, it has been well-documented that the measured global warming during the 25-year period of 1970-1994 was accompanied by a downturn in Atlantic basin major hurricane activity over what was experienced during the 1930s through the 1960s.
We attribute the heightened Atlantic major hurricane activity between 1995-2005 to be a consequence of the multidecadal fluctuations in the Atlantic Ocean thermohaline circulation (THC) as we have been discussing in our Atlantic basin seasonal hurricane forecasts for several years. Major hurricane activity in the Atlantic has been shown to undergo marked multidecadal fluctuations that are directly related to North Atlantic sea surface temperature anomalies. When the Atlantic Ocean thermohaline circulation is running strong, the central Atlantic equatorial trough (ITCZ) becomes stronger. The stronger the Atlantic equatorial trough becomes, the more favorable are conditions for the development of major hurricanes in the central Atlantic. Since 1995, the THC has been flowing more strongly, and there has been a concomitant increase in major hurricanes in the tropical Atlantic.
There have been similar past periods (1940s-1950s) when the Atlantic was just as active as in recent years. For instance, when we compare Atlantic basin hurricane numbers of the last 15 years with an earlier 15-year period (1950-64), we see no difference in hurricane frequency or intensity even though the global surface temperatures were cooler and there was a general global cooling during 1950-64 as compared with global warming during 1990-2004."
Arguments for a link between global warming and increased hurricane intensity are summarized in this short video segment produced by PBS: Is global warming making hurricanes more intense?
Much of the material presented in this section is taken from
Normalized Hurricane Damage in the United States: 1900-2005
authored by Pielke, Jr. et al., published in Natural Hazards Review, Vol. 9, No. 1, February 1, 2008.
A summary of their work, taken from the paper's abstract is provided below:
After more than two decades of relatively little Atlantic hurricane activity, the past decade saw
heightened hurricane activity
and more than $150 billion in damage in 2004 and 2005.
This paper normalizes mainland U.S. hurricane damage from 1900-2005 to 2005 values ...
A normalization provides an estimate of the damage that would occur if storms from the past made
landfall under another year's societal conditions. Our methods use changes in inflation
and wealth at the national level and changes in
population and housing units at the coastal county level. Across both normalization methods,
there is no remaining trend of increasing
absolute damage in the data set, which follows the lack of trends in landfall frequency or
intensity observed over the twentieth century.
The 1970s and 1980s were notable because of the extremely low amounts of damage compared to other
decades. The decade 1996 to 2005
has the second most damage among the past 11 decades, with only the decade 1926 to 1935 surpassing its costs.
The most
damaging single storm is the 1926 Great Miami storm, with $140-157 billion of normalized damage:
the most damaging years are 1926
and 2005. Of the total damage, about 85% is accounted for by the intense hurricanes
Saffir-Simpson Categories 3, 4, and 5 , yet these
have comprised only 24% of the U.S. landfalling tropical cyclones.
The study normalizes property damages over the years by making three major adjustments: one to account for inflation, one for growth in wealth (to account for fact that people generally have more "stuff" today as compared to the past and the real value of all this "stuff" has increased), and one to account for overall population growth along affected coastlines. It is very important to consider all three adjustments. Several past works have only considered the inflation adjustment and end up with a plot like figure 3 (from Pielke 2008), which shows that even after adjusting for inflation, total property loses in the US from tropical cyclones continues to follow an upward trend through 2005. However, this is very misleading, since much of the increased costs can be attributed to increases in wealth and population density. Some have even used a plot like figure 3 as evidence that global warming is resulting in stronger hurricanes in the US.
The US coastal populations are certainly more vulnerable to property damage today compared to
past times due to the rapid population increases, especially along the "warm weather coasts"
(see figure 2, Pielke 2008), as well as the tendency for building more lavish structures on the
coasts. After considering these factors, Pielke finds no trend with time in the absolute damage
caused by US landfalling hurricanes. The following summary and warning for the future is taken
from the conclusion:
it
should be clear from the normalized estimates that while 2004
and 2005 were exceptional from the standpoint of the number of
very damaging storms, there is no long-term trend of increasing
damage over the time period covered by this analysis. Even Hurricane
Katrina is not outside the range of normalized estimates for
past storms. The analysis here should provide a cautionary warning
for hurricane policy makers. Potential damage from storms is
growing at a rate that may place severe burdens on society. Avoiding
huge losses will require either a change in the rate of
population growth in coastal areas, major improvements in
construction standards, or other mitigation actions. Unless such
action is taken to address the growing concentration of people and
properties in coastal areas where hurricanes strike, damage will
increase, and by a great deal, as more and wealthier people
increasingly inhabit these coastal locations.
There need to be discussions about whether or not we as a society should continue to build-in and populate hurricane prone areas. Given that people desire to live right on warm water coasts and the very high short-term value available to investors and politicians, it would seem very unlikely to me that we as a society will not continue to build new and more lavishly on coastlines that are vulnerable to hurricanes. Another possibility is to regulate through building codes that all structures be able to withstand the worst possible hurricane, but this is quite costly as well. We will probably have to accept that hurricanes will cause major property damage from time to time. One thing that should not be ignored is that urban areas on coastlines should not become so densely populated and congested that evacuations in a reasonable time become impossible. Urban planners need to have reliable evacuation plans.
Should hurricane damaged areas be rebuilt? Who should pay for the rebuilding? Current practice is for the federal government to reimburse people for their losses due to natural disasters. Thus most rebuild in the same disaster-prone area. In a sense the federal government encourages people to rebuild at a large cost to taxpayers. My opinion is that government should not outlaw building in hurricane prone areas, but the people that build in these areas have to assume the risks involved, that is, find private insurance or risk losing everything, i.e., don't expect to be bailed out with tax money. On the other hand, there are those who believe hurricane damages should be a shared public risk assumed by all taxpayers.
Although tropical storms and hurricanes are responsible for more economic damage per year in the US than any other type of severe weather, in general they have been responsible for relatively small numbers of deaths in recent decades compared with the early decades of the 1900s. The explanation for the decreasing trend in deaths is simple ... In the early part of the century before satellite imagery and sophisticated forecasting methods, people had little warning of an approaching hurricane, and many were killed. In fact the Galveston, TX hurricane of 1900 still ranks as the most deadly in U.S. history with from 8 to 12 thousand deaths. In modern times, people are warned of an approaching storm and either evacuate or make necessary preparations.
Of course, Katrina was the exception to this trend. Katrina forces us to reconsider the long-held belief that hurricanes will not cause many deaths in the United States because we have such a great hurricane monitoring system and no storm will catch anyone by surprise. Sure property damage was high, but we have come to expect that. The question here is Even with the ample warning provided by the National Hurricane Center, why did so many people die as a result of Katrina? Last count is over 1300 confirmed deaths. This is the most deaths related to a single hurricane since 1928. There are several reasons for the large loss of life from Katrina. Undoubtedly the vulnerability of the New Orleans area to levee failure and flooding was a strong contributing factor and had Katrina hit somewhere else there would have been less loss of life. However, the biggest contributing factor was the decisions made by many people to ignore evacuation warnings and remain home for the storm.
Yes, federal and local government screwed up in their response to the disaster, but the only sure way to save lives is for people to evacuate before the storm hits. One reason I heard over and over from survivors is that they did not leave because they didn't think things could get that bad. This reaction is probably due to the several factors: (1) major hurricanes don't strike very often; (2) many residents were either new to the gulf coast or never experienced a major hurricane before; (3) some had stayed and lived through other hurricanes, thinking that they are no big deal; and (4) some had evacuated for previous storms that may have missed their house or turned out to be not that severe, so they refused to leave this time. I am sure we can come up with some others. In my opinion, individuals need to educate themselves and make responsible decisions for themselves, their families, and anyone else who relies on them. People living in hurricane prone areas need to understand the devastion that hurricanes can cause, keep informed on hurricane activity in their area, and be prepared to make intelligent decisions. People in New Orleans had the additional responsibility to understand the vulnerability of their city to the possibility of levee breaks whenever a major storm is near. On the other hand, others believe that government should take on more of the responsibility to make sure that people evacuate.
Unfortunately, a Katrina-type disaster was foreseen by many people. In fact a New Orleans newspaper published an article in 2001 about a devasting senario very close to what actually happened. Others just warned about how the people living in hurricane-prone areas seemed unware of the potential damage that can occur when major hurricanes make landfall and would not take appropriate action. Quoting the sumarizing statement from a report generated by the National Hurricane Center (which was prepared prior to the 2004 and 2005 monster hurricane seasons):
"In virtually every coastal city of any size from Texas to Maine, the present National Hurricane Center Director, Max Mayfield, has stated that the United States is building toward its next hurricane disaster. The population growth and low hurricane experience levels of many of the current residents, form the basis for this statement. The areas along the United States Gulf and Atlantic coasts where most of this country's hurricane related fatalities have occurred are also now experiencing the country's most significant growth in population. This situation, in combination with continued building along the coast, will lead to serious problems for many areas in hurricanes. Because it is likely that people will always be attracted to live along the shoreline, a solution to the problem lies in education, preparedness and mitigation.
The message to coastal residents is: Become familiar with what hurricanes can do, and when a hurricane threatens your area, increase your chances of survival by moving away from the water until the hurricane has passed! Unless this message is clearly understood by coastal residents through a thorough and continuing preparedness effort, disastrous loss of life is inevitable in the future."
We can be otpimistic about the well organized and rather smooth evacuations that took place before the powerful Hurricane Ike struck in 2008, which in large part was due to the memory of Katrina. In the near future I do not think we will see a hurricane death toll in the US like Katrina. However, after we go through another slow period in Atlantic hurricanes, like 1970-1995, will people remember how potentially deadly hurricanes can be?