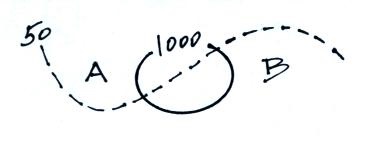
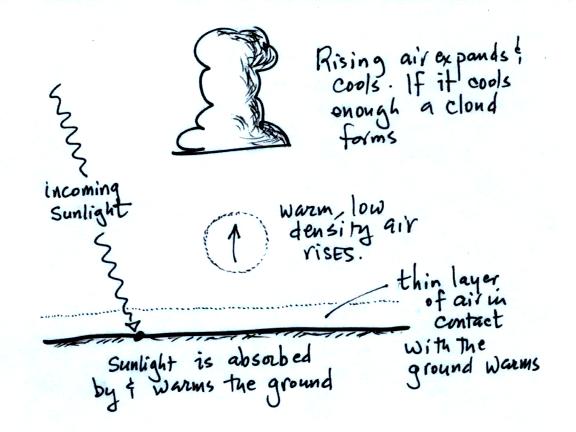
Convergence and divergence. Rising
air motions, what can cause air to rise and why is rising
air. Sinking air. Strong and weak pressure
gradients and their effects.

| Tue., Oct. 14 |
4:00 - 5:00 pm |
Haury (Anthropology) 129 |
| Wed., Oct. 15 |
4:00 - 5:00 pm |
Haury (Anthropology) 216 |