Week #5 Assignment
1. This property of electromagnetic radiation
is inversely proportional to temperature. If temperature increases
_______ decreases.
a. propagation speed
b. intensity c. rate of emission
d. wavelength of peak emission
2. The wavelength of peak emission from a tungsten
lightbulb is about 1 micrometer. Is the bulb HOTTER
or COLDER
than the surface of the sun? Is
the peak emission from the bulb VISIBLE or
INVISIBLE light?
3. The wavelength of peak emission from the sun is
determined largely by the sun's
a. age b.
temperature c. composition d.
size
4. Which of the following are not found in the
infrared portion of the spectrum? (more than one answer)
a. 0.4 to 0.7 micrometer interval
b. the atmospheric window
c. peak emission from the sun
d. peak emission from the earth
5. Which of the following are true when the earth
is in radiative equilibrium? (more than one answer)
a. the earth absorbs 100% of the
incoming sunlight
b. the earth does not emit any
electromagnetic radiation into space
c. the temperature of the earth
remains constant
d. the earth gains and loses energy
at equal rates
6. A in the figure below represents incoming
sunlight energy that is absorbed by the earth. R is reflected
sunlight energy
and E is the radiation
that is emitted by the earth. Which of the following equations
will apply when the earth is in
radiative equilibrium?

7. Fill in each blank below with
VIS(visible), IR(infrared), or UV(ultraviolet).
strong absorption by
O2 and O3 in the air_______
peak emission
from the sun is found in the_______
selective absorption by CO2 and
H2O__________
the atmospheric window is in the_______
8. ____________________ is the most
abundant greenhouse gas in the earth's atmosphere.
9. A window is a wavelength interval
where the atmosphere TRANSMITS ABSORBS
REFLECTS EMITS
electromagnetic
radiation.
10. About 50% of the sunlight reaching the top
of the atmosphere is
a. absorbed by
ozone b. reflected by air molecules
and clouds
b. absorbed by the
earth's surface d. absorbed by
greenhouse gases in the air
11. Thick cloud cover will generally result in
HIGHER LOWER nighttime temperatures and HIGHER
LOWER daytime
temperatures than
would be observed on a day with clear skies.
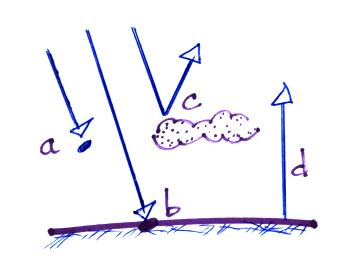
12. Which ray of light in the figure below will not
have any effect on the surface temperature? (rays a and b are absorbed
by the atmosphere and
the ground, respectively; ray c is reflected by a cloud, and ray d is
light emitted by the earth's
surface)
13. Which of the following best describes
the effects of clouds on visible and infrared light?
a. clouds are good
absorbers of IR and visible light
b. clouds are good reflectors of visible and IR light
c. cloud absorb IR
light and reflect visible
light
d. clouds reflect IR light and absorb visible light
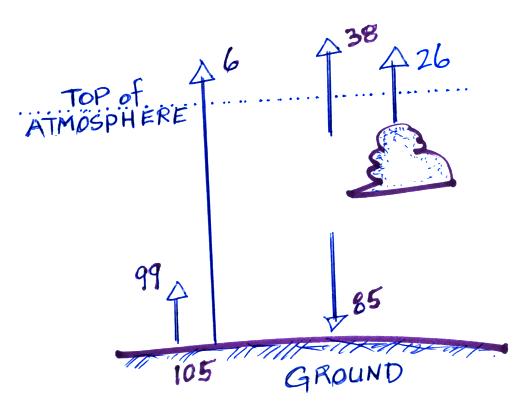
14. The figure below shows the earth's surface
emitting 105 units of electromagnetic radiation; 99 units are absorbed
by greenhouse gases in
the atmosphere and 6 units pass through the atmosphere into
space. The atmosphere is
emitting 38 units
upward into space and 85 units downward toward the surface.
Clouds emit 26 units upward
into space. What
must be added to the figure below to bring it into radiative equilbrium?