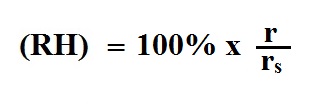Humidity variables review
1.
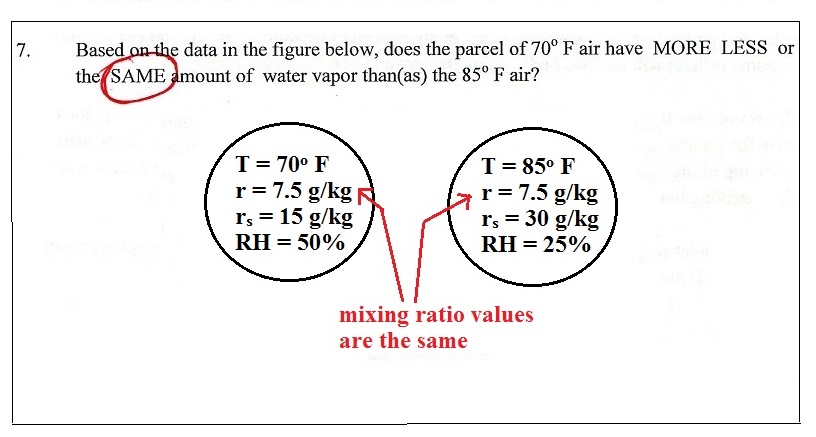
Mixing ratio has units of grams per kilogram (g/kg)
Here's another couple of questions (and answers) from the
in-class optional assignment
If you cool the air enough you can cause water vapor to start
to condense. The air is losing water vapor, the amount of
water vapor in the air is decreasing. Mixing ratio will
decrease in that case. Also because the dew point
temperature also gives you an idea of how much water vapor is
actually in the air, answer (d) would also be acceptable.
2.
Saturation mixing ratio also has units of grams/kilogram.
You can look the value of saturation mixing ratio up in a chart
(like the one of p. 84 in the ClassNotes)
Here are a few more questions from the optional assignment
3.
The relative humidity really doesn't tell you how
much water vapor is actually in the air.
4.
The dew point temperature has a couple of
jobs. Here's the one we'll be using today
Cooling air doesn't change the mixing
ratio. As you cool air the saturation mixing ratio
decreases. Eventually the values of the mixing ratio and
saturation mixing ratio become equal and the RH becomes 100%.
This is the dew point's other job. One of the example
problems will try to show that if you know the dew point
temperature you can easily figure out the mixing ratio and
vice versa.