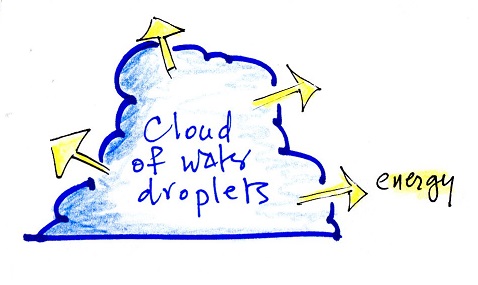
Here are three examples showing
energy originally hidden in water vapor reemerging in a
tornado, water rushing down a mountain or wash, and a
hurricane. A big portion of the energy in tornadoes,
flash floods, and hurricanes was initially hidden in the
water vapor.
2. Energy units
Next just brief mention of energy units
Joules
are the units of energy that you would probably
encounter in a physics class. We'll
usually be using calories as units of energy. 1
calorie is the energy need to warm 1 gram of water 1 C
(there are about 5 grams of water in a
teaspoon).
Here's a little miscellaneous information that you
don't need to worry about remembering. You've
probably seen the caloric content of food on food packages
or on menus in restaurants. 1 "food calorie" is
actually 1000 of the calories mentioned above. Food
is probably a form of chemical energy, the energy is
released when the food is consumed.

A 150 pound person would burn
almost 500 food calories while sleeping during the
night (8 hours x 60 minutes per hour x 1 food
calorie per minute). This is about the energy
contained in one donut.
3. Energy transport processes
By far the most important energy
transport process, at least as far as the atmosphere is
concerned, is at the bottom of the list above. Energy
transport in the form of electromagnetic radiation (sunlight
for example) is the only process that can transport energy
through empty space. Electromagnetic radiation travels
both to the earth (from the sun) and away from the earth
back into space. Electromagnetic radiation is also
responsible for about 80% of the energy
transported between the ground and atmosphere.
You might be surprised to learn that latent heat is the
second most important transport process. This term
latent heat can refer to both a type of energy and an energy
transport process (the energy is hidden in the water vapor,
the water vapor can move around and carry that energy with
it).
Rising parcels of warm air and sinking parcels of cold
air are examples of free convection. Wind is an
example of convective energy transport. Because of
convection you feel colder or a cold windy day than on a
cold calm day (the wind chill effect). Ocean
currents are also an example of convection.
Convection is also one of the ways of rising air motions
in the atmosphere (convergence into centers of low pressure
and fronts are two other ways we've encountered so
far). Convection is one of
four energy transport processes, convection is one of
four ways of causing air to rise.
Conduction is the least important energy transport at
least in the atmosphere. Air is such a poor conductor
of energy that it is generally considered to be an
insulator.