ATMO 336 -- Exam 1 (110 possible points) Name: ______________________________
Multiple
Choice Questions (Answer All 30 Questions) -- 3 Points Each.
1. The two gases that are mainly responsible for the
atmospheric greenhouse effect are ______.
(a) nitrogen and oxygen (c)
oxygen and ozone
(b) carbon dioxide and ozone (d) carbon dioxide and water vapor
2. Which two gases are most abundant in the Earth’s
atmospheric?
(a) nitrogen and oxygen (c)
oxygen and ozone
(b) carbon dioxide and ozone (d)
carbon dioxide and water vapor
3. Which two molecules prevent harmful UV radiation from
penetrating to the surface?
(a)
nitrogen and oxygen (c) oxygen and ozone
(b)
carbon dioxide and ozone (d)
carbon dioxide and water vapor
4. Which heat transfer mechanism propagates energy from
the sun to reach Earth?
(a)
advection (b)
convection (c)
conduction (d) radiation
5. Without an atmosphere, Earth’s daytime temperatures
would be much hotter and its nighttime lows would be much colder. (True / False)
6. If the temperature of an object doubles, then the
wavelength of maximum radiation that is emitted by the object would _____?
(a) increase by a factor of 2 (b) decrease by a
factor of 2 (c)
increase by a factor of 16 (d)
decrease by a factor of 16
7. If the temperature of an object doubles, then the
total radiation that is emitted by the object would _____?
(a) increase by a factor of 2 (b) decrease by a factor of 2 (c)
increase by a factor of 16 (d) decrease by a factor of 16
8. If an air parcel’s temperature remains constant but
its density doubles, then its pressure would _____?
(a) increase by a factor of 2 (b) decrease by a
factor of 2 (c) increase
by a factor of 16 (d) decrease
by a factor of 16
9. Which process cools the surrounding environment?
(a) condensation (Gas à Liquid) (b) evaporation (Liquid à Gas) (c)
deposition (Gas à Vapor)
10. Raindrops falling from clouds can evaporate before
hitting the ground. (True / False)
11. If the air temperature is 60° F and the dew point
temperature is 30° F, what percentage of the air is composed of water vapor?
(a)
50% (b)
30% (c) less than 4 %
12. When you can “see your breath” on a cold morning, you
are seeing an air parcel that contains _____.
(a) a high concentration of water vapor coming from your
mouth (c) a
high concentration of CO2 coming from your mouth
(b) a low concentration of O2 coming from your
mouth (d) tiny droplets of liquid water
13. Albuquerque NM is 1631 m (5352 ft) above sea
level. Las Vegas NV is 663 m (2174
ft) above sea level. Which city
will have the lowest station air pressure measured with a barometer?
(a) Albuquerque (b)
Las Vegas (c)
sometimes Albuquerque, sometimes Las Vegas.
14. Sea level pressure that is plotted on a surface
weather map for Las Vegas is _____ than the station pressure measured with a
barometer.
(a)
always lower (b)
always higher (c)
sometimes lower, sometimes higher
15. Higher than about 20,000 ft above sea level, people
have trouble breathing. The main
reason is that the _____.
(a) air pressure and density are too low to get enough oxygen (c) percentage
of oxygen molecules in the air drops below 21%
(b)
air temperature is too cold to breathe (d)
ozone levels are too high
16. The geostrophic wind results from a balance between
which two forces?
(a) Coriolis-friction (b) Coriolis-pressure gradient (c)
Friction-pressure gradient (d)
Coriolis-centripetal
17. Consider a glass of ice water. If no water condenses
onto the outside of the glass, the dew point temperature of the air would most
likely be?
(a) Below 0° C (b)
Exactly 0° C (c)
Above 0° C
18. Why does a metal object at room temperature (70° F) often feel colder to the touch than a wooden
object at a same temperature?
(a) Metal is a better heat conductor than wood (c)
Metal is a better radiator than wood
(b)
Wood is a better heat conductor than metal (d)
Wood is a better heat convector than metal
19. On a given day, the wind chill equivalent temperature
in Chicago IL is lower than it is in Boston MA. Which of the following MUST be true?
(a) The air temperature in Chicago is lower than it is in
Boston
(b) The wind speed in Chicago is faster than it is in
Boston
(c) The rate of heat loss from the human body is slower in
Chicago than it is in Boston
(d) The rate of heat loss from the human body is
faster in Chicago than it is in Boston
20. On a given day, the heat index in Atlanta is higher than
it is in Tucson. Which of the
following MUST be true?
(a)
The air temperature in Atlanta is higher than it is in Tucson
(b)
The dew point in Atlanta is higher than it is in Tucson
(c) The rate of heat loss from the human body is slower in Atlanta
than it is in Tucson
(d)
The rate of heat loss from the human body is faster in Atlanta than it is in
Tucson
Use the table of
saturation mixing ratios to answer questions the next three questions. This is
the same table you used in homework #3.
21. If the air at a temperature of 100° F and a dew point
temperature of 60° F, then the relative humidity would be closest to?
(a)
16% (b) 26% (c)
36% (d)
46%
22. If the air temperature is 70° F and the relative
humidity is 85%, then the dew point temperature would be closest to?
(a)
35° F (b)
45° F (c)
55° F (d)
65° F
23. If the air temperature is 80° F and the wet-bulb
temperature is 59° F, then the actual mixing ratio would be?
(a) 5.28 g/kg (b) 7.74
g/kg (c)
11.10 g/kg (d)
22.43 g/kg
24. If the wet-bulb temperature is 65° F and the
saturation mixing ratio is 13.38g/kg, then the dew point temperature would be?
(a) below 65° F
(b)
above 65° F (c) exactly 65° F
|
Temperature (ºF) |
Saturation Mixing Ratio (g/kg) |
Temperature (ºF) |
Saturation Mixing Ratio (g/kg) |
|
5 |
1.21 |
55 |
9.32 |
|
10 |
1.52 |
60 |
11.19 |
|
15 |
1.89 |
65 |
13.38 |
|
20 |
2.34 |
70 |
15.95 |
|
25 |
2.88 |
75 |
18.94 |
|
30 |
3.54 |
80 |
22.43 |
|
35 |
4.33 |
85 |
26.48 |
|
40 |
5.28 |
90 |
31.16 |
|
45 |
6.40 |
95 |
36.56 |
|
50 |
7.74 |
100 |
42.78 |
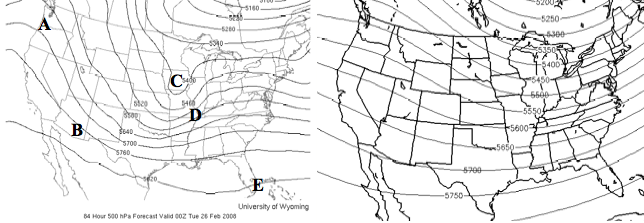
Locate the five points
labeled A, B, C, D and E on the 84 hour, 500 mb forecast map (left); use that
map and the February climatology map (right) to answer the following six
questions.
25. Which point is located under a trough? C (By far, the best choice. It is located in the largest
negative height anomaly.)
26. At which point would you expect temperatures to be the
most above average? A (Location of the largest positive height anomaly)
27. At which point would you expect the best chance for
precipitation? D (Downwind of the
trough)
28. At which point would you expect to find the fastest
winds at 500 mb? D (Tightest spacing
between height contours)
29. This map is forecast for 00Z on Tuesday, Feb 26. What is the local time in Tucson?
(a)
12 AM, Feb 26 (b)
12 PM, Feb 26 (c)
5 AM, Feb 26 (d) 5 PM, Feb 25
30. What type of weather would you predict for Tucson AZ,
point B?
(a)
Sunny, cool (b) Sunny, warm (c)
Rainy, cool (d)
Rainy, warm
Short Answer Questions
(Select 4 of the 7 Questions) -- 5 Points Each
Write your answers on the
attached blank sheet(s). Let us
know if you need more paper. Your
answers should be concise and to the point. No more than a few sentences (2 or 3) should be needed. Make sure you answer all parts of each
question. Points will be
deducted for incorrect or unnecessary statements in your answer, even if the
correct answer is found somewhere. Use legible penmanship; if the graders
can’t read it, then they can’t (and won’t) award credit. Be sure to clearly indicate which 4
questions you would like graded.
1.
Explain why winds only
10 m above the ground tend to blow from higher to lower pressure, but they do
not more than 1 km above the ground.
Winds are geostrophic above 1 km elevation,
and the geostrophic wind blows perpendicular to the pressure gradient force
(PGF). At 10 m above ground level, friction slows the wind speed to below the
geostrophic value, which in turn makes the Coriolis force smaller than the PGF;
the imbalance between the PGF and Coriolis forces would accelerate the air to
lower pressure.
2.
Cyclones can deepen only
underneath regions of upper-level divergence. Explain why divergence is necessary for a cyclone to
develop.
Deepening, or decreasing surface pressure,
can occur only if the total mass in the air column directly over the cyclone
decreases with time. Only net divergence in the column can evacuate air from
the column.
3.
The color of an electric
coil on a stove top changes colors from red, to orange, then yellow as it is
warms up to the full setting. Explain why.
Wien’s Law states that the wavelength of
maximum radiation emission becomes shorter as the temperature increases. Red
light corresponds to a longer wavelength than orange light, which in turn
corresponds to a longer wavelength than yellow light.
4.
A thermos contains a
“dead” air space (i.e. still air) between its reflective inner liner and its
outer case. Explain the two main ways that its construction serves to impede
heat transfer from the hot contents that are inside the liner to the colder air
that is outside the thermos’ shell.
Air has a very low specific heat capacity,
which means conductive heat transfer between the liner and outer shell would be
small. Still air implies that convective heat transfer, which requires fluid
motion for mass exchange, would be close to zero.
5.
People who move to the
desert southwest from much more humid and much colder regions of the United
States often say things like “40° (Fahrenheit) sure feels a lot colder here than it did
back home.” There is actually some
truth to this statement. Keeping
in mind that even when you are not obviously sweating, water is constantly
moving from tissues beneath the skin to the skin surface, explain the above
perception. (NOTE: I am not looking for answers like
“their blood thins” or “those folks just aren’t used to cold anymore.”)
The evaporation of water from your flesh
occurs at a faster rate in dry air (all other factors being equal). Evaporation
requires heat from the surrounding environment, which is supplied by your
flesh. You would feel this as a
colder temperature.
6.
In sauna rooms, people
can spend several minutes in conditions of air temperature over 90° C (194° F) with a relative humidity near 10%. However, if you stick your arm into
liquid water that is at a temperature of 90° C (194° F), you would be severely burned in much less than
one minute. Give two reasons why
people are able to spend time in a sauna, but they are severely burned by water
at the same temperature.
1) Sweating would be a very effective
cooling mechanism in hot arid air, but it cannot exist if your arm is submerged
in water. 2) Water has a much higher heat capacity than air. Thus, water would
cool at a very slow rate in response to heat transfer from to your arm compared
to the air next to your arm.
7.
List the two main ways
that the human body responds to heat stress (body core temperature getting too
high) and briefly describe how they work.
List the two main ways the human body responds to cold stress (core
temperature getting too low) and briefly describe how they work.
Fighting hyperthermia: 1) Increased sweating
would increase evaporative cooling. 2) Vasodilation would increase blood flow
and heat transport from the body core to the extremities, and thus it would
cool the body core.
Fighting hypothermia: 1) Involuntary shivering increases metabolism, which generates internal heat. 2) Vasoconstriction would reduce blood flood and heat transport from the body core to the extremities, and thus it would slow the rate of cooling.