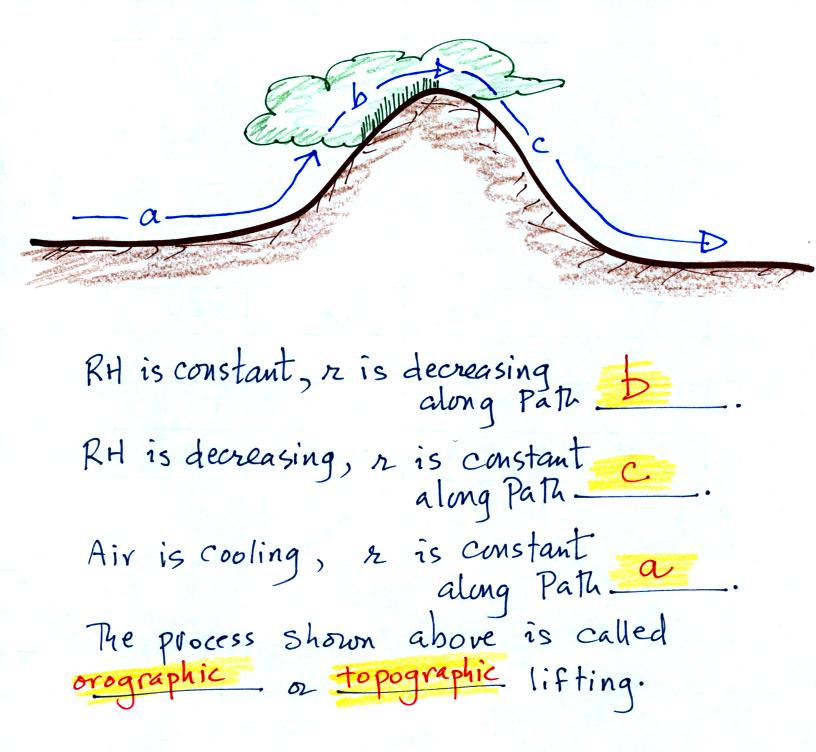
The air begins to rise along Path a. Rising air expands and
cools. As the air cools, the relative humidity will increase, but
the mixing ratio remains constant along Path a.
Path a ends and Path b begins when the RH becomes 100%, the rising air
has cooled to its dew point. The air continues to rise and cool
along Path b. Water vapor begins to condense and fall to the
ground as rain. Because the air is losing moisture, the mixing
ratio will decrease. The RH remains constant at 100%.
Path c begins when the air begins to flow downhill. Sinking air
is compressed and warms. The RH will drop below 100% and the
cloud disappears. No moisture is added to or removed from the air
along Path c. The mixing ratio will remain constand and the
relative humidity is decreasing as the air warms along Path c.
