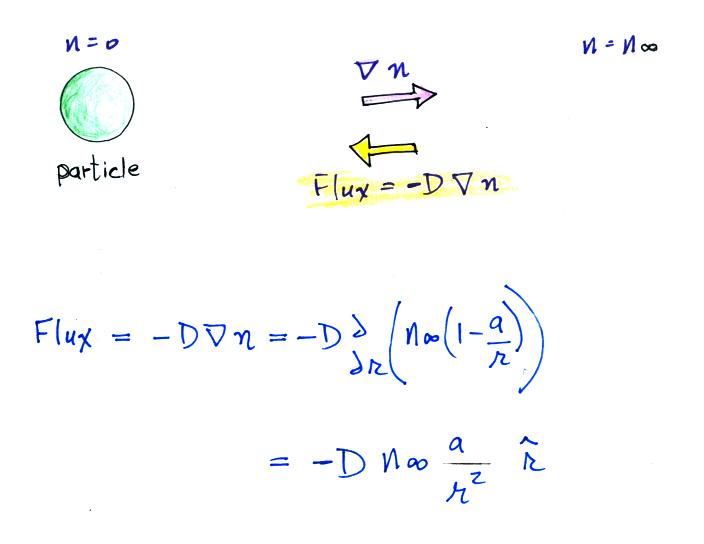
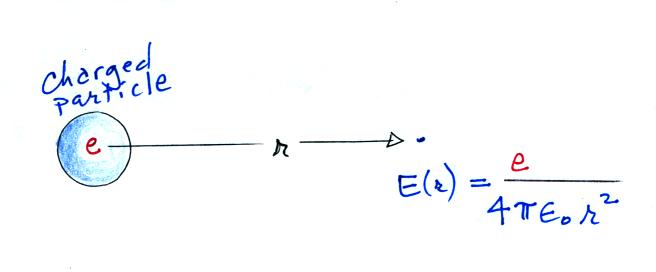
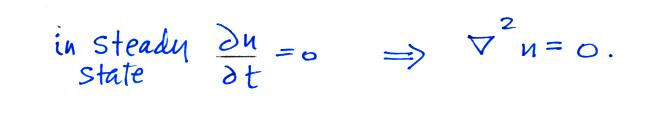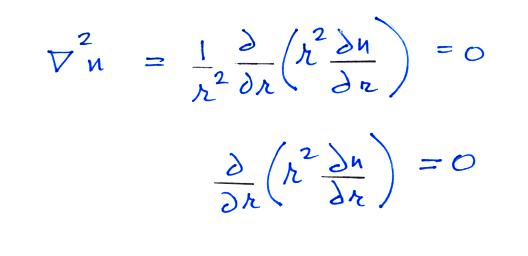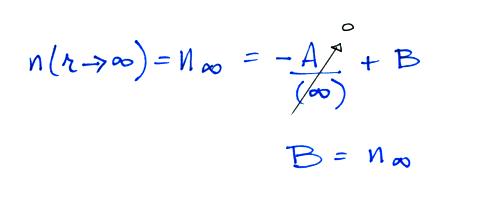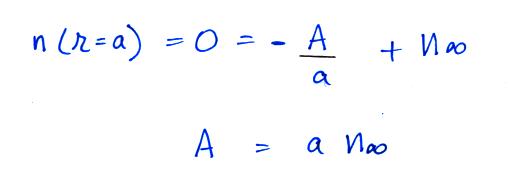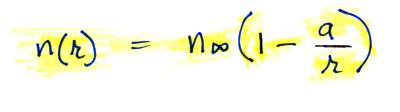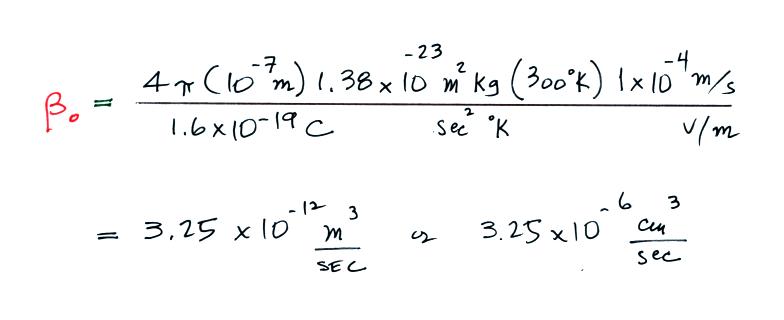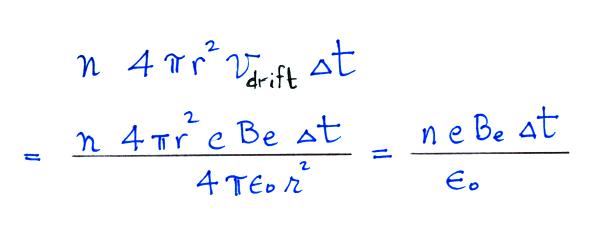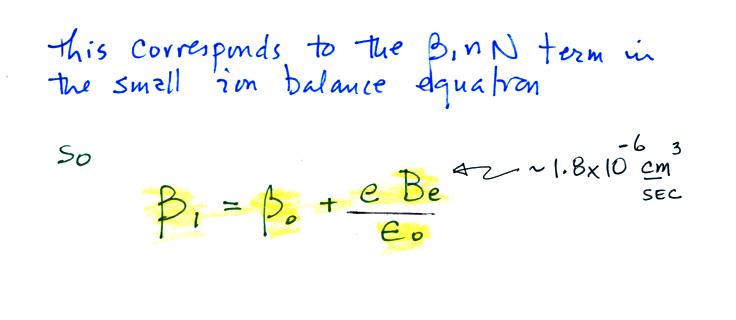Next we find the total number of
particles moving inward toward the particle by multiplying the flux by
the area of a sphere with radius r surrounding the particle
We assume these small ions are all collected by the
particle. We've only considered a single particle at this point,
so to
determine the total rate of loss of small ions we need to multiply by
the concentration No of uncharged
particles.
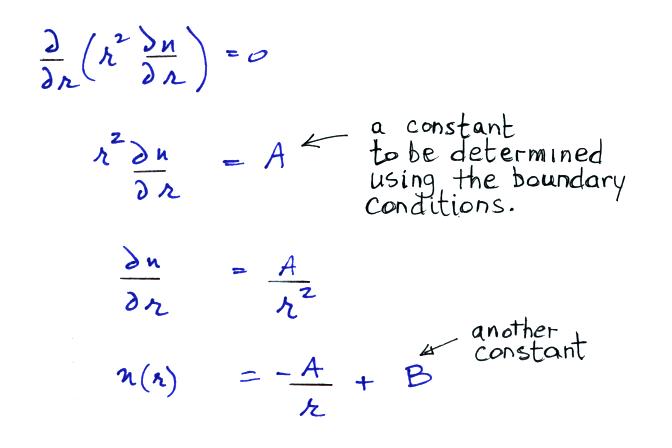
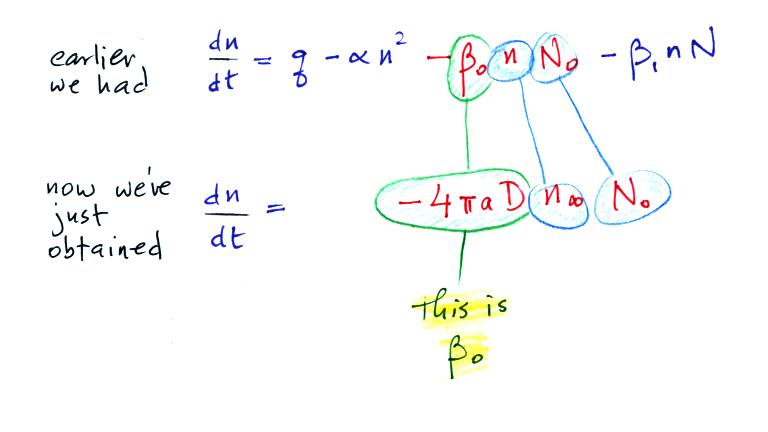
Now let's go back and write down the small ion balance equation
again
By comparing the small ion loss
expression we've just derived with the corresponding term in the small
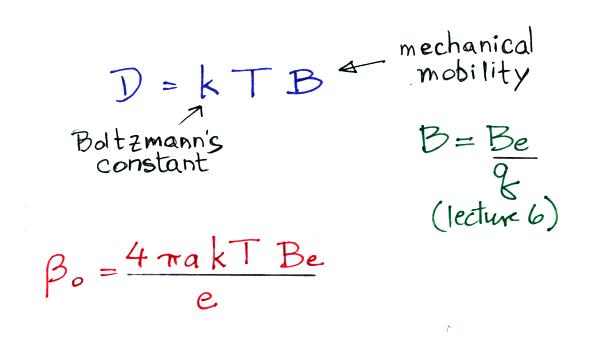
ion balance equation we can see that βo = 4 π a D
An expression for the diffusion coefficient, D, can be derived using
principles from kinetic theory and is
The top expression above is also know as the Einstein
(or
Einstein-Smoluchowski)
Relation.
Here's an
example calculation where we assume a particle radius of 0.1 μm (10-7 m) and an electrical mobility of 1
x 10-4 (m/s)/(V/m).