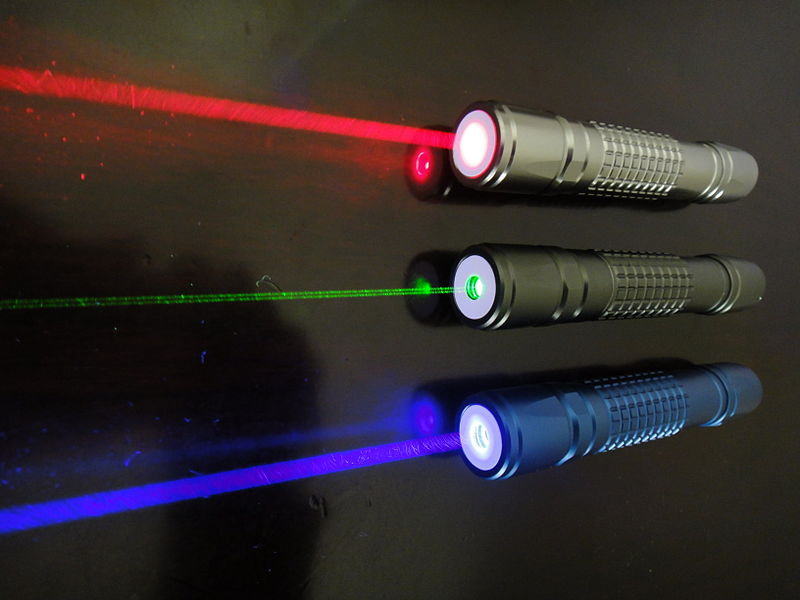
Friday Feb. 26, 2016
Eva Cassidy "American Tune"
(4:09), Crooked Still "American Tune"
(3:25), Black Prairie "Nowhere
Massachusetts" (3:20), Punch Brothers "Sometimes"
(4:57)
An In-class
Optional Assignment was handed out today and collected at
the end of class. If you weren't in class and would like to
do the assignment you can download using the link at left.
If you turn in the assignment at the beginning of class next
Monday you will receive at least partial credit (as with all
Optional Assignments you should have the assignment done before
coming to class).
Energy transport by electromagnetic
radiation
It's time to tackle electromagnetic (EM)
radiation, the 4th and most important of the energy transport
processes (it's the most important because it can transport
energy through empty space (outer space)).
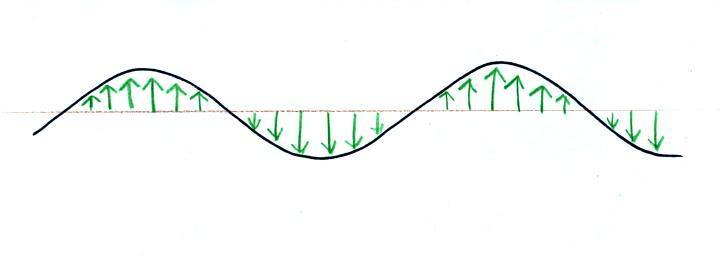
Many introductory textbooks depict EM
radiation with a wavy line like shown above. They don't
usually explain what the wavy line represents.
The wavy line just connects the tips of a
bunch of "electric field arrows". But what exactly are electric
field arrows?
Static electricity and electric fields

To understand electric
fields we need to first step back and review a
couple of rules concerning static electricity.
That won't take too long, static
electricity is something you're most likely already familiar
with.
Believe it or not there is even a National Static
Electricity Day (Jan. 9).
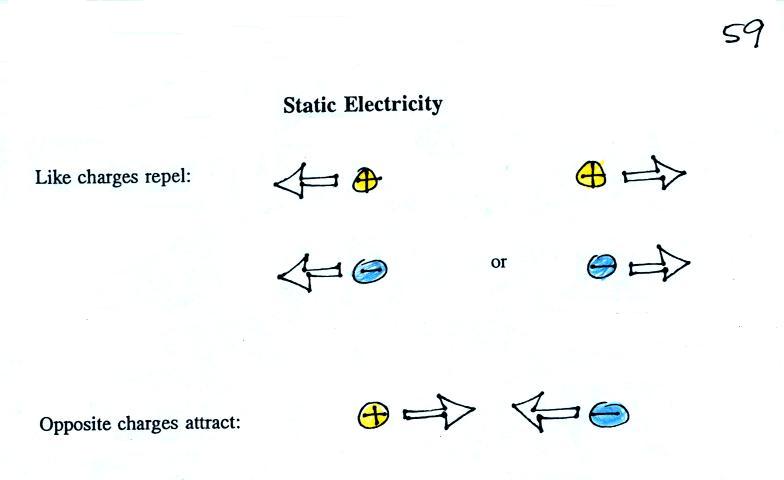
The static
electricity rules are found at the top of p. 59 in the
photocopied ClassNotes
Two electrical charges with the same polarity (two positive
charges or two negative charges) push each other apart.
Opposite charges are attracted to each other.
Here
are some pictures I found online.

|

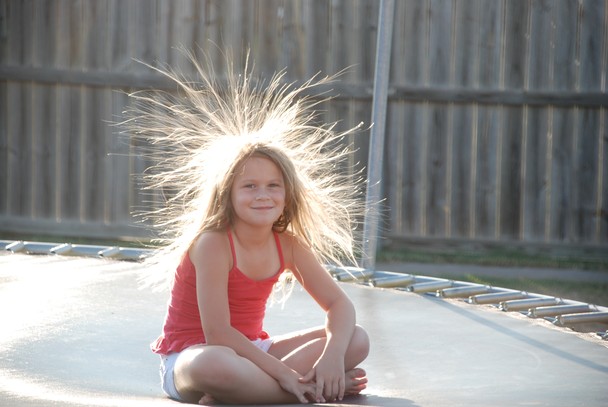
|
This girl became charged with static
electricity while jumping on a trampoline and
illustrates the repulsive force of like charges.
Her hair and body are all charged up with charge of the
same polarity. The individual hairs are trying to
get as far away from each other as they can. This
photo was a National Geographic Magazine 2013
Photo Contest winner (source)
People's hair will sometimes stand on end
under a thunderstorm. That is a very dangerous
situation to be in.
|
A cat covered in Styrofoam
"peanuts". Here the cat and the
"peanuts" have opposite charges and are attracted
to each other. (source)
Being a cat owner I would worry about the cat
swallowing one of the peanuts and possibly choking.
|
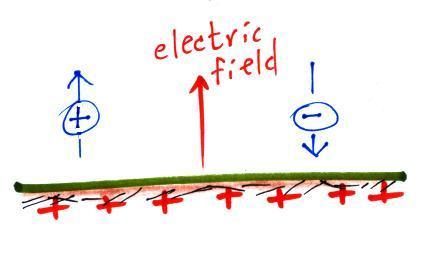
An electric
field arrow (vector)
just shows the direction
and
gives you an idea of the strength
of the electrical force
that would be exerted on a positive
charge at that position.
It's just like an arrow painted on a drive showing you what
direction to drive.
Here are a couple of questions to test your
understanding.
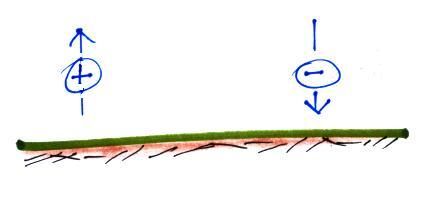
First what polarity of charge must be on ground to cause the
charges in the figure below to move as they are doing.
Would the electric field arrow in the air just above the ground
point UPWARD, point DOWNWARD, or would the electric field arrow be
ZERO?
Here's a second perhaps somewhat harder question
What is the direction of the electric field arrow at Point X halfway between a +
and a - charge.
You'll find answers to both questions at the end of today's notes.
Electromagnetic (EM) radiation
Now we'll use what we know about electric field arrows (electric
field for short) to start to understand electromagnetic
radiation. How is it able to carry energy from
one place to another. You'll find most of the following on
p. 60 in the photocopied ClassNotes.
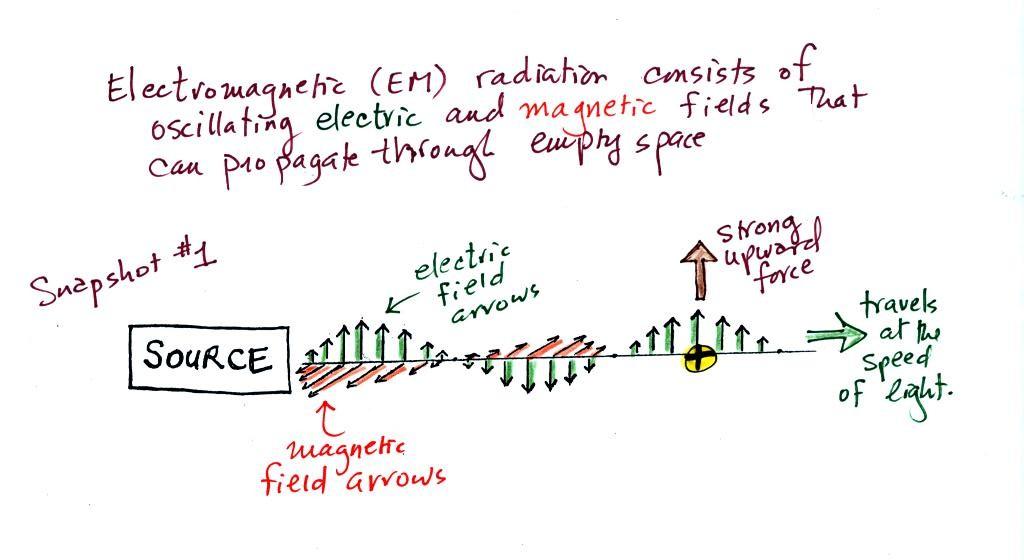
We imagine turning on a source of EM radiation and then a
very short time later we take a snapshot. In that time the
EM radiation has traveled to the right (at the speed of
light). The EM radiation is a wavy pattern of electric and
magnetic field arrows. We'll ignore the
magnetic field arrows. The E field arrows sometimes point
up, sometimes down. The pattern of electric field arrows
repeats itself.
Note the + charge near
the right side of the picture. At the time this picture
was taken the EM radiation exerts a fairly strong upward force
on the + charge (we use
the E field arrow at the location of the + charge to determine the
direction and strength of the force exerted on the + charge).
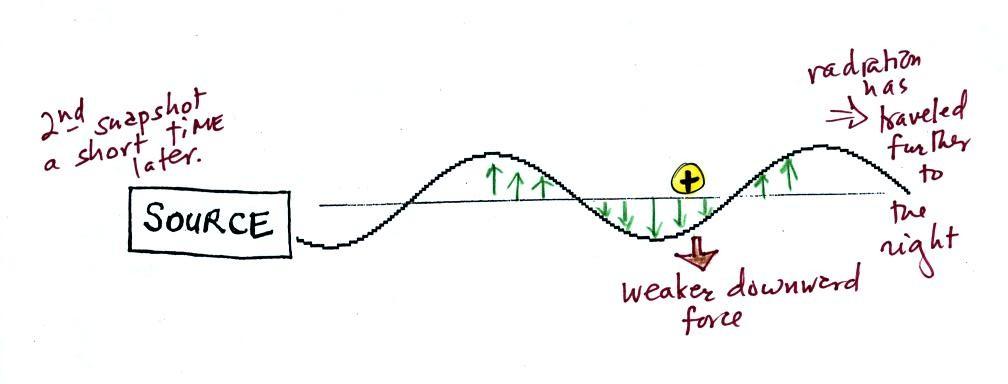
This picture above was taken a short time after the first
snapshot after the radiation had traveled a little further to
the right. The EM radiation now exerts a somewhat weaker
downward force on the +
charge.
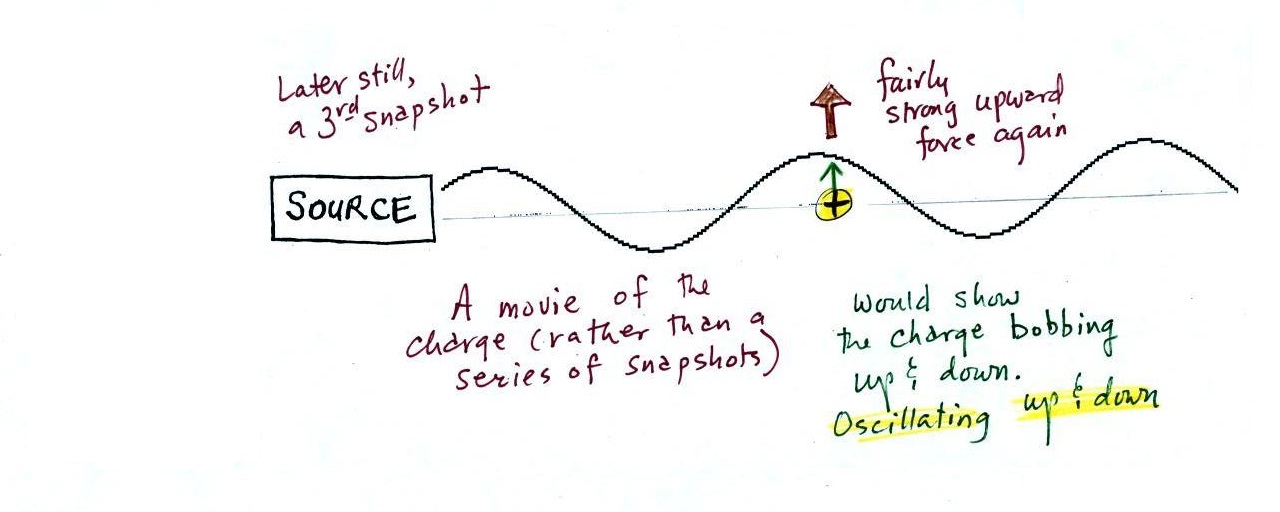
A 3rd snapshot taken a short time later. The + charge is now being pushed
upward again.
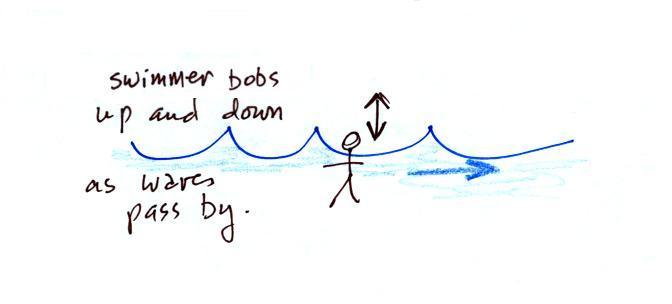
A movie of the + charge,
rather than just a series of snapshots, would show the charge
bobbing up and down much like a swimmer in the ocean would do as
waves passed by.
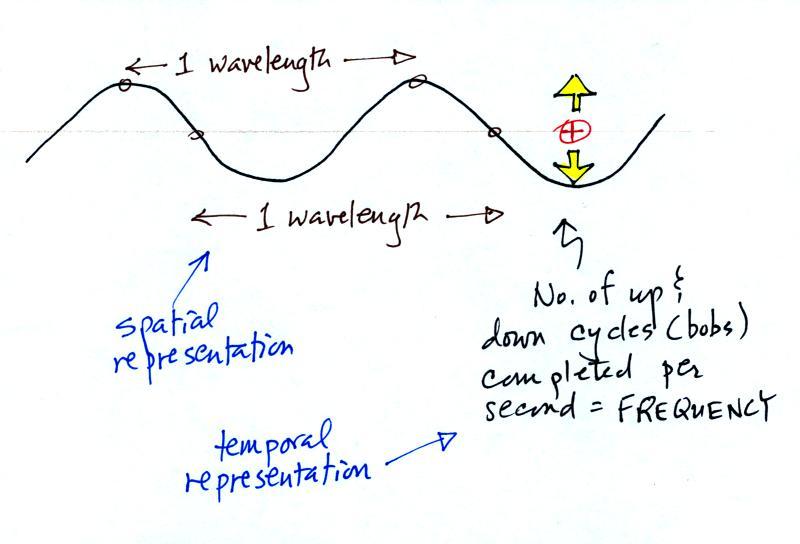
Wavelength and frequency
The wavy pattern used to depict EM radiation can be
described spatially
(what you would see in a snapshot) in terms of its wavelength,
the distance between identical points on the pattern.
Or you can describe the radiation temporally
using the frequency of oscillation (number of up and down cycles
completed by an oscillating charge per second). By
temporally we mean you look at one particular fixed point and
look at how things change with time.
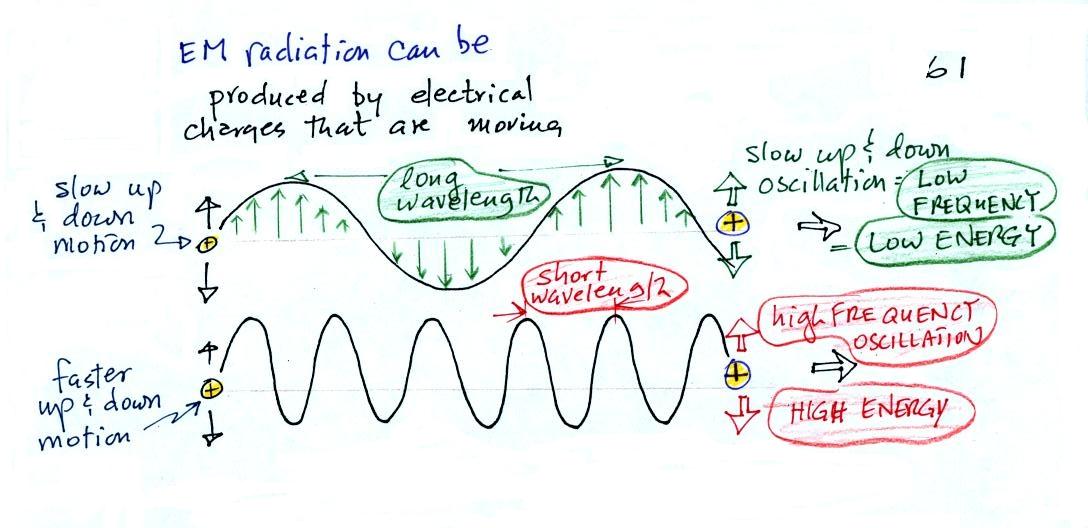
Wavelength, frequency, and energy
EM radiation can be created when you cause a charge to
move up and down. If you move a charge up and down
slowly (upper left in the figure above) you would produce long
wavelength radiation that would propagate out to the right at the
speed of light. If you move the charge up and down more
rapidly you produce short wavelength radiation that propagates at
the same speed.
Once the EM radiation encounters the charges at the right side
of the figure above the EM radiation causes those charges to
oscillate up and down. In the case of the long wavelength
radiation the charge at right oscillates slowly. This is low
frequency and low energy motion. The short wavelength causes
the charge at right to oscillate more rapidly - high frequency and
high energy.
These three characteristics: long
wavelength / low frequency / low energy go
together. So do short wavelength / high
frequency / high energy. Note that the two
different types of radiation both propagate at the same speed.
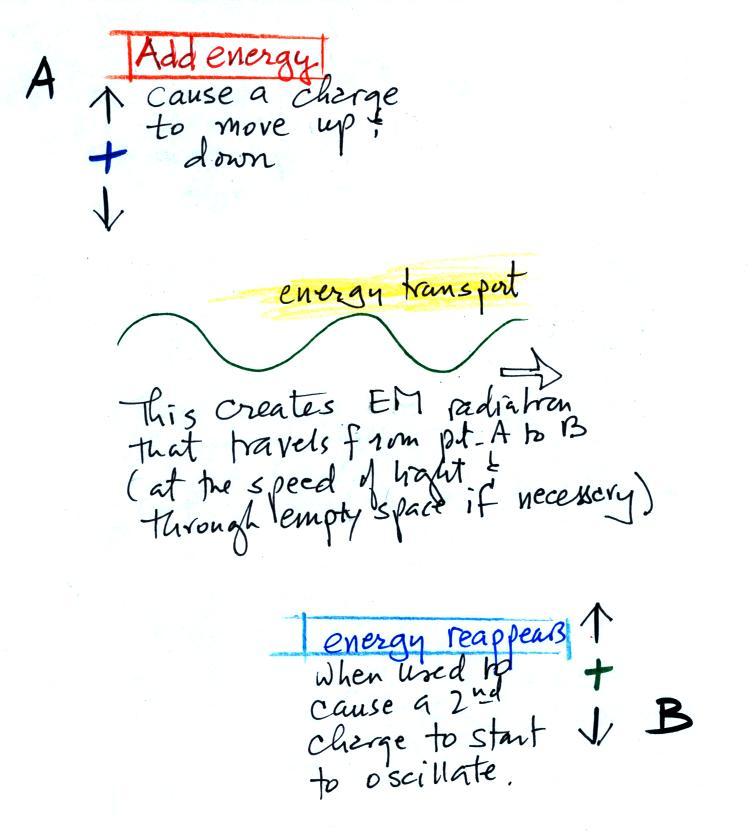
The
following figure illustrates how energy can be transported
from one place to another (even through empty space) in the
form of electromagnetic (EM) radiation.
You add energy when you cause an
electrical charge to move up and down and create the EM
radiation (top left).
In the middle figure, the EM
radiation that is produced then travels out to the right (it
could be through empty space or through something like the
atmosphere).
Once the EM radiation encounters an electrical charge at
another location (bottom right), the energy reappears as the
radiation causes the charge to move. Energy has been
transported from left to right.
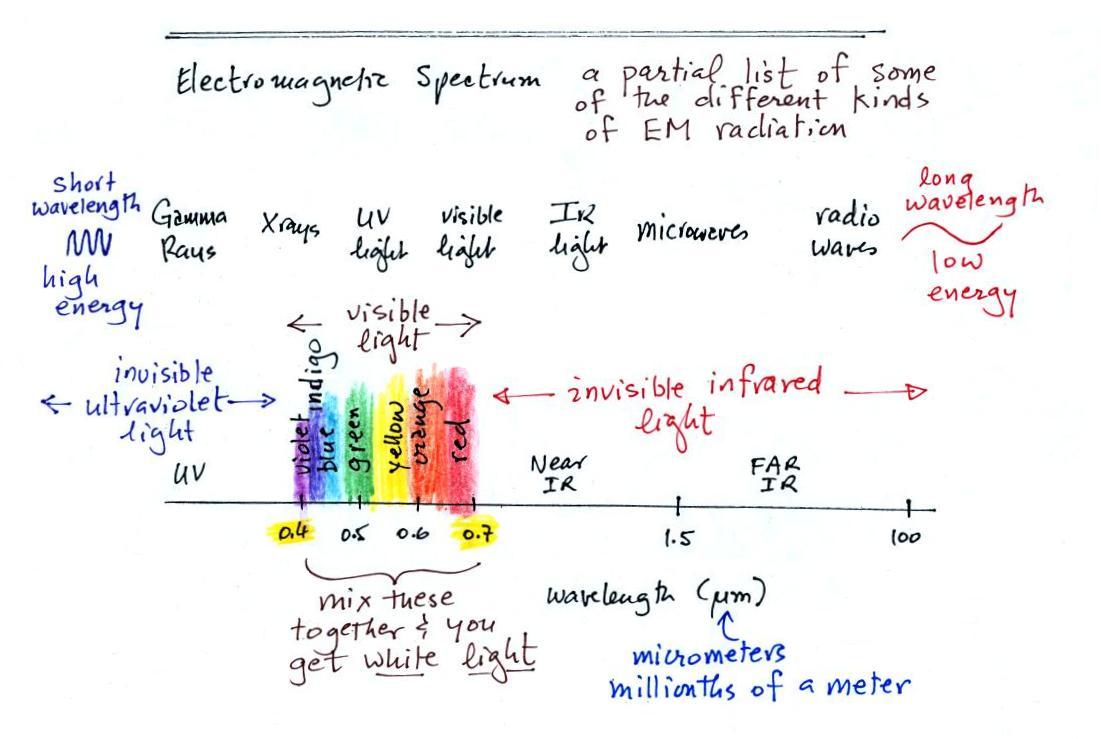
The electromagnetic spectrum
The EM spectrum is just a list of the different kinds of EM
radiation. A partial list is shown below.
In the top list, shortwave wavelength/high energy forms of EM
radiation are on the left (gamma rays and X-rays for
example). Microwaves and radiowaves are longer
wavelength/lower energy forms of EM radiation.
We will mostly be concerned with just ultraviolet light (UV),
visible light (VIS), and infrared light (IR). These are
shown on an expanded scale below. Note the micrometer
(millionths of a meter) units used for wavelength for these kinds
of light. The
visible portion of the spectrum falls between 0.4 and 0.7
micrometers. UV and IR light are both
invisible. All of the vivid colors shown above are just EM
radiation with slightly different wavelengths. When you see
all of these colors mixed together, you see white light.
I've tried to demonstrate colors mixing together to make white
light using laser pointers.
But it's too hard to get them adjusted so that the small spots
of colored light all fall on top of each other on the screen at
the front of the room. And even if you do the small spot of
light is so small that it's hard to see clearly in a large
classroom (you need to do the experiment on a piece of paper a few
feet away).
Here's the basic idea, you mix red green and blue light
together. You see white light were the three colors overlap
and mix in the center of the picture above.
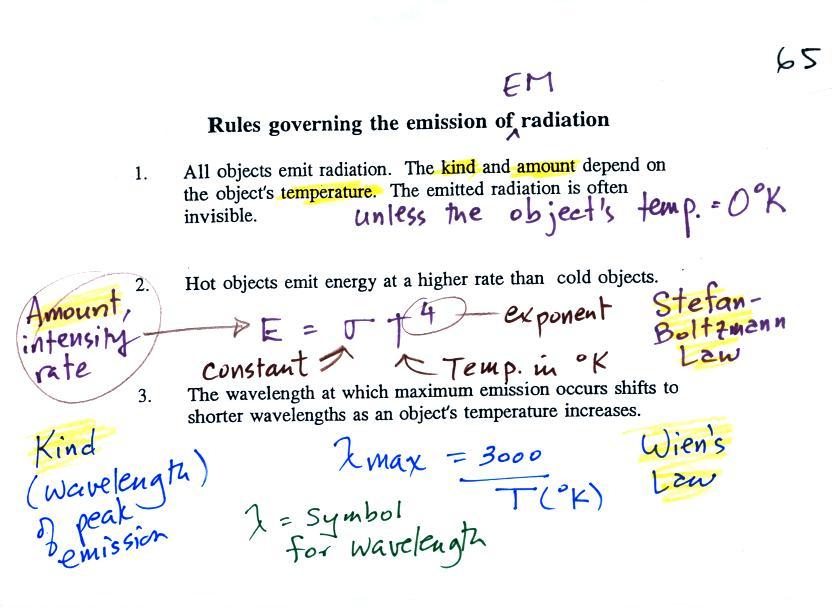
Rules governing the
emission of EM radiation
We spent most of the rest of
the class learning about some rules governing the emission of
electromagnetic radiation. Here they are:
1.
Everything
warmer than 0 K will emit EM radiation. Everything in
the classroom: the people, the furniture, the walls and the
floor, even the air, are emitting EM radiation.
Often this radiation will be invisible so that we can't see it
and weak enough that we can't feel it (or perhaps because it
is always there we've grown accustomed to it and ignore
it). Both the amount and kind (wavelength) of the
emitted radiation depend on the object's temperature. In
the classroom most everything has a temperature of around 300
K and we will see that means everything is emitting infrared
(IR) radiation with a wavelength of about 10µm.
2.
The second rule allows you to determine the
amount of EM radiation (radiant energy) an object will
emit. Don't worry about the units (though they're given
in the figure below), you can think of this as amount, or
rate, or intensity. Don't worry about σ (the Greek character rho) either, it is
just a constant. The amount depends
on temperature to the fourth power. If the temperature
of an object doubles the amount of energy emitted will
increase by a factor of 2 to the 4th power (that's 2 x 2 x 2 x
2 = 16). A hot object just doesn't emit a little more
energy than a cold object it emits a lot more energy than a
cold object. This is illustrated in the following
figure:
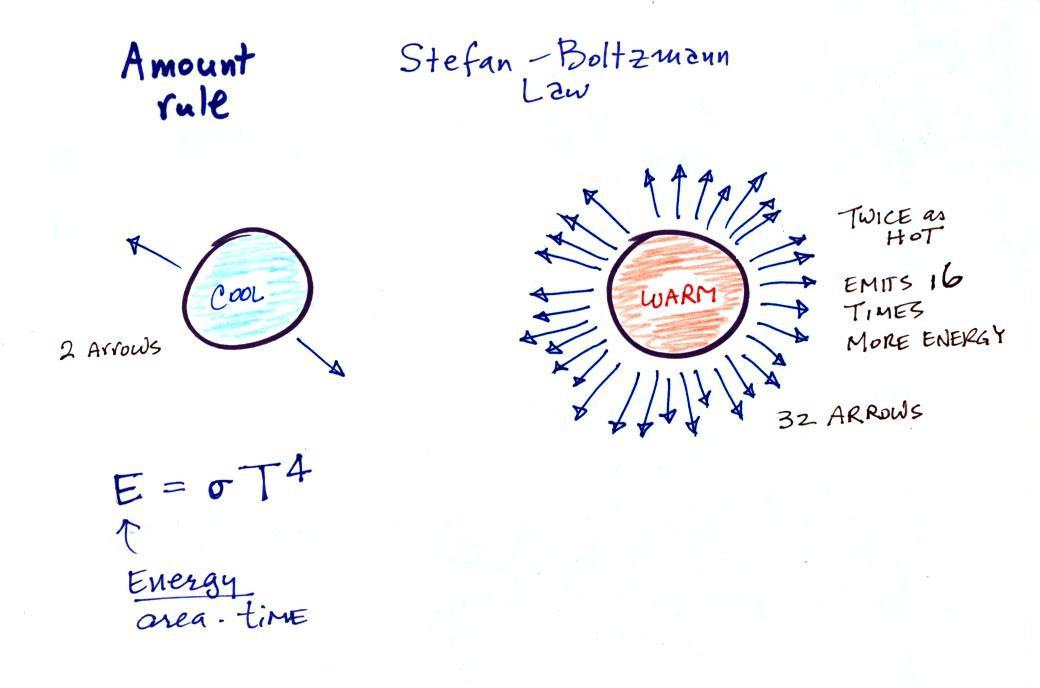
The cool object is emitting 2
arrows worth of energy. This could be the earth at 300
K. The warmer object is 2 times warmer, the earth heated
to 600 K. The earth then would emit 32 arrows (16 times
more energy).
The earth has a temperature of 300 K. The sun is 20
times hotter (6000 K). Every square foot of the sun's
surface will emit 204 (160,000)
times more energy per second than a square foot of the
earth's surface.
3.
The third rule tells you something about the kind of
radiation emitted by an object. We will see that objects
usually emit radiation at many different wavelengths but not in
equal amounts. Objects emit more of one particular
wavelength than any of the others. This is called λmax
("lambda max", lambda is the Greek character used to represent
wavelength) and is the wavelength of maximum emission. The
third rule allows you to calculate λmax.
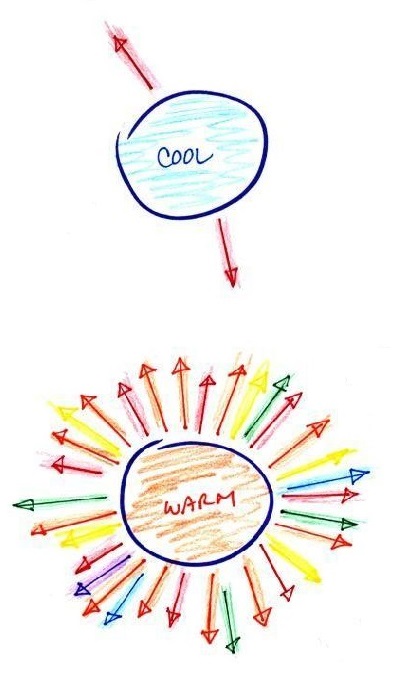
The tendency for warm objects to emit radiation at shorter
wavelengths is shown below.
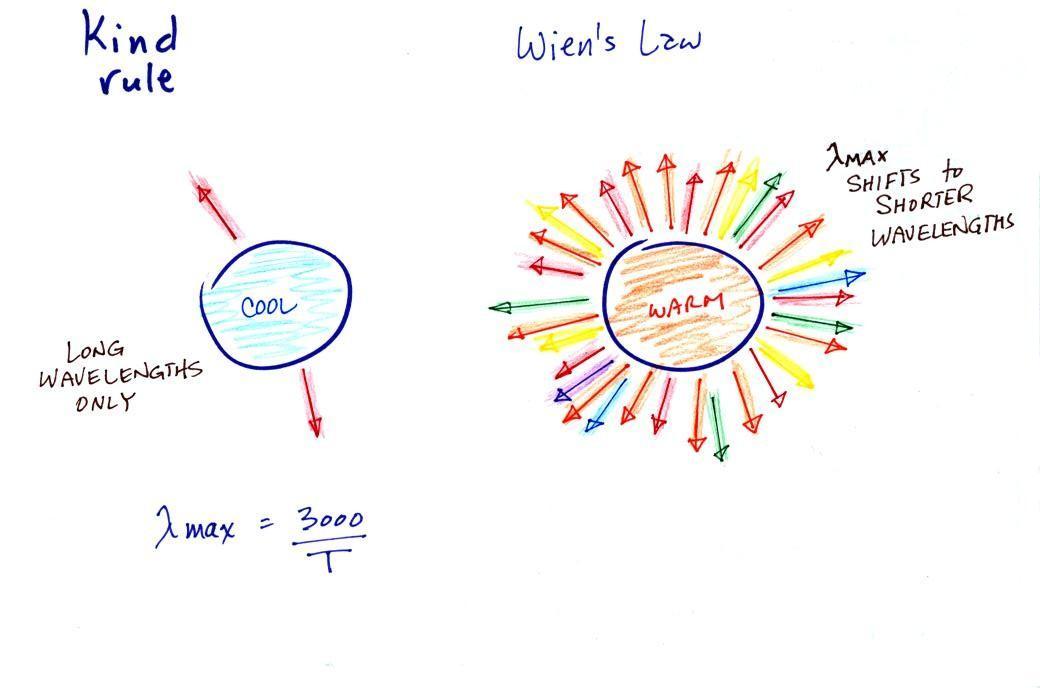
The cool object could be emitting infrared light
(that would be the case for the earth at 300 K). It might be
emitting a little bit of red light that we could see. That's
the 2 arrows of energy that are colored red. The warmer
object will also emit IR light but also shorter wavelengths such
as yellow, green, blue, and violet (maybe even some UV if it's hot
enough). Remember though when
you start mixing different colors of visible light you get
something that starts to look white. The cool object
might appear to glow red, the hotter object would be much
brighter and would appear white.
Here's another way of understanding Stefan Boltzmann's law and
Wien's Law (the graph
below is on the bottom of p. 65 in the ClassNotes).
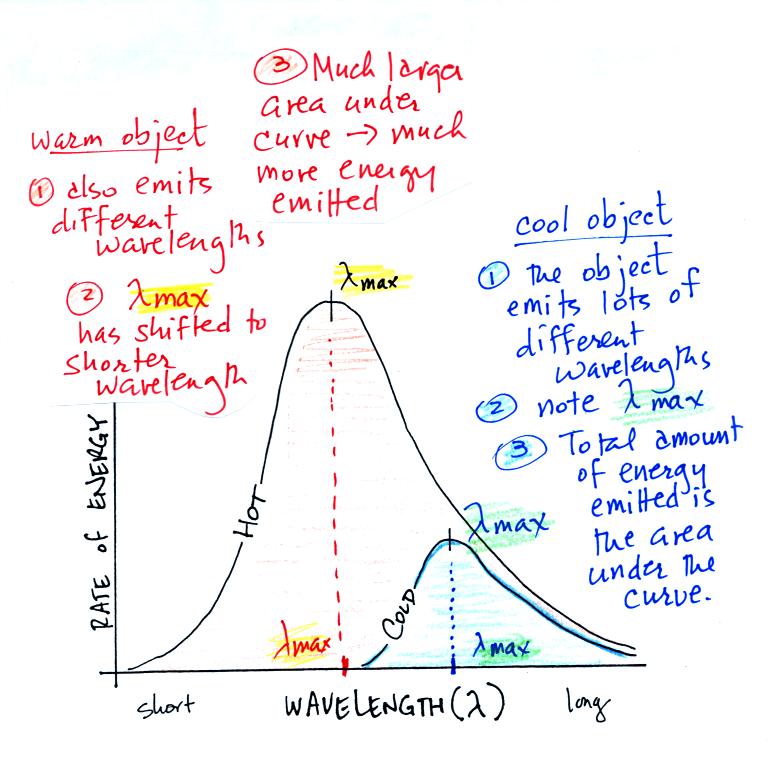
1.
Notice
first that both and warm and the cold objects emit radiation
over a range of wavelengths (the curves above are like quiz
scores, not everyone gets the same score, there is a
distribution of grades). The warm object emits all the
wavelengths the cooler object does plus lots of additional
shorter wavelengths.
2.
The peak of
each curve is λmax
the wavelength of peak emission (the
object emits more of that particular wavelength than any other
wavelength). Note that λmax
has shifted toward shorter wavelengths for the warmer
object. That is Wien's law in action. The warmer
object is emitting lots of types of short wavelength radiation
that the colder object doesn't emit.
3.
The area under the curve is the total radiant
energy emitted by the object. The area
under the warm object curve is much bigger than the area
under the cold object curve. This
illustrates the fact that the warmer object emits a lot more
radiant energy than the colder object.
It is relatively easy to see Stefan-Boltzmann's law and Wien's
Law in action. The class demonstration consisted of an
ordinary 200 W tungsten bulb is connected to a dimmer switch (see
p. 66 in the photocopied ClassNotes). We'll be looking at
the EM radiation emitted by the bulb filament.
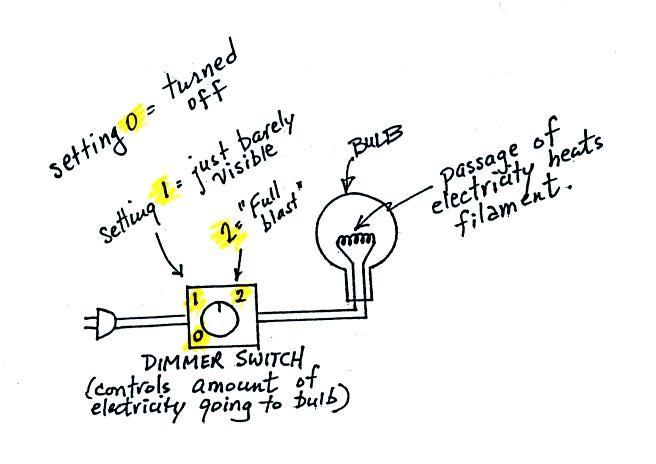
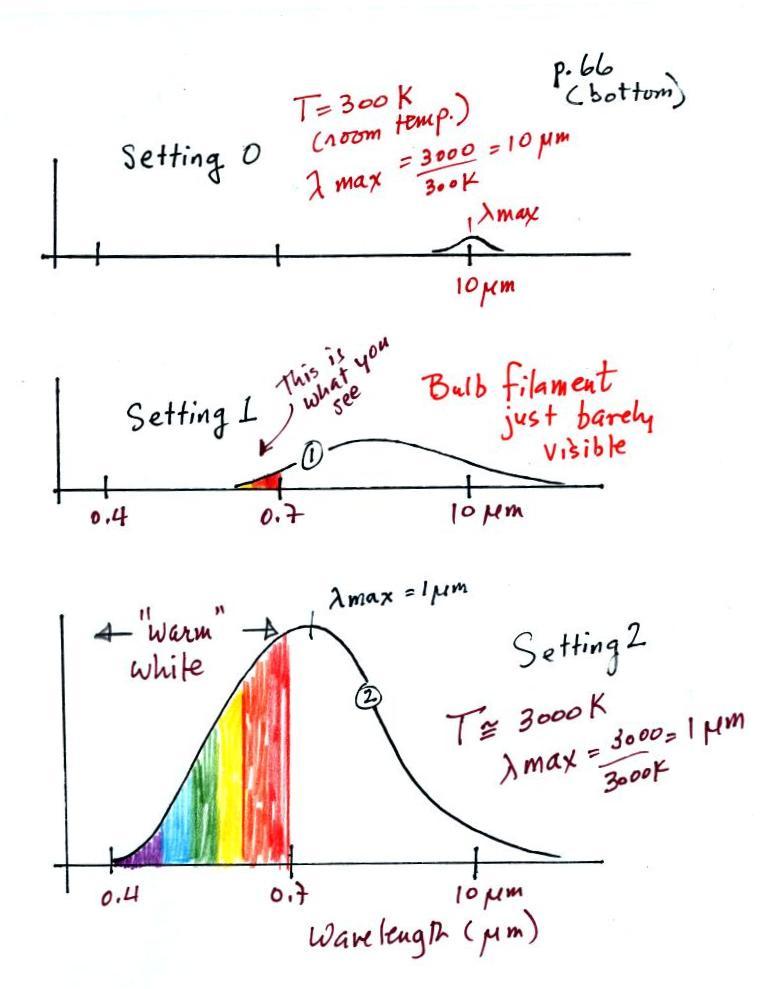
The graph at the bottom of p. 66
has been split up into 3 parts and redrawn for improved clarity.
We start with the bulb turned off (Setting 0). The
filament will be at room temperature which we will assume is
around 300 K (remember that is a reasonable and easy to remember
value for the average temperature of the earth's surface).
The bulb will be emitting radiation, it's shown on the top graph
above. The radiation is very weak so we can't feel
it. We can use Wien's Law to calculate the
wavelength of peak emission, λmax
. The wavelength of peak emission
is 10 micrometers which is long wavelength, far IR radiation so we can't
see it.
Next we use the dimmer switch to just barely turn the bulb on
(the temperature of the filament is now about 900 K). The
bulb wasn't very bright at all and had an orange color.
This is curve 1, the middle figure. Note the far left end
of the emission curve has moved left of the 0.7 micrometer mark
- into the visible portion of the spectrum. That is what
you were able to see, just the small fraction of the radiation
emitted by the bulb that is visible light (but just long
wavelength red and orange light). Most of the radiation
emitted by the bulb is to the right of the 0.7 micrometer mark
and is invisible IR radiation (it is strong enough now that you
could feel it if you put your hand next to the bulb).
Finally we turn on the bulb completely (it is a 200 Watt bulb
so it got pretty bright). The filament temperature is now
about 3000K. The bulb is emitting a lot more visible
light, all the colors, though not all in equal amounts.
The mixture of the colors produces a "warm white" light.
It is warm because it is a mixture that contains a lot more red,
orange, and yellow than blue, green, and violet light. It
is interesting that most of the radiation emitted by the bulb is
still in the IR portion of the spectrum (lambda max is 1
micrometer). This is invisible light. A tungsten
bulb like this is not especially efficient, at least not as a
source of visible light.
You were able to use one of the diffraction gratings handed
out in class to separate the white light produced by the bulb
into its separate colors.
When you looked at the bright white bulb filament through one
of the diffraction gratings the colors were smeared out to the
right and left as shown at left below.
You may need to rotate the slide 90 degrees to see the spectrum
as shown above.
Here are the answers to the two electric field questions
embedded earlier in the notes.
#1. The ground can be either negatively or positively
charged. If the ground were negatively charged the positive
charge would be attracted to the ground and the
negative charge repelled and pushed upward. That's not
what is happening. So the ground must be positively charged.
The positive charge is creating the force that causes the
positive charge to move upward. So that too must be
direction that the electric field arrow is pointing.
#2. To begin to answer the question we
imagine placing a + charge at Point X.
The center charge will be repelled by the charge on the left
and attracted to the charge on the right. The center charge
would move toward the right.
The electric field arrow shows the direction of the force on
the center charge. Since we've determined the
+ charge will move to the right,
that's the direction the electric field arrow
should point. The electric field arrow will point toward the
right.