Quiz #2 Study Guide
click
here to
download in a more printer friendly format
Energy, temperature
and heat (10 pts). Kinetic
energy
-
energy of motion. Temperature (which scale?)
provides a measure of the average kinetic energy of the atoms or
molecules in a substance. Heat energy is the total kinetic energy
of all the atoms or molecules in a material. Energy units:
calories.
What is the relationship between energy added to (or removed from) an
object, ΔE, and the
temperature change, ΔT,
that
results? Specific heat or thermal capacity. Water has a
relatively high specific heat (4 or 5 times higher than soil). A
city on a coastline will have a more moderate climate (what does that
mean?) than a city
located further inland. Other than a change in temperature what
else can happen when energy is added to or removed from a material?
Temperature
scales
(15 pts).
Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin (absolute)
scales.
You should know the temperatures of the boiling point of water at sea
level and the melting point of ice/freezing point of
water on the F and C scales. The global
average surface temperature of the earth is about what
temperature on the Kelvin scale?
Energy
transport
(40 pts).
(1) Conduction (10 pts). Energy is transported from hot
to cold by
random
atomic or molecular motions at a rate that depends on the material
(thermal conductivity)
and the temperature gradient. Examples of good and poor conductors. An
object with high thermal conductivity will often feel cold to the
touch because it rapidly conducts energy away from your body (our
perception of temperature is not a good measurement of temperature).
(2) Convection (15 pts). Energy transport by organized motion of atoms
or
molecules (works in gases and liquids but not solids). Free (rising and
sinking air) and forced
convection. Free convection is a third way of causing rising air
motions in the atmosphere. Wind chill temperature.
(3)Latent heat energy transport (15 pts). 2nd most
important
energy transport process. Six phase change
names. For
each phase change you should know whether energy is added to a material
(absorbed
from or taken from the surroundings) or taken from
the material (released into the
surroundings).
Sample
Questions (from the Fall
2000 Quiz Packet):
Quiz #1: 5, 12,
EC3 Final Exam: 12, 43,
53 See also this new set of Sample Questions
Static
electricity and
electric fields (5 pts). Like
charges
repel,
opposite
charges
attract.
The
pattern
of
electric
field
vectors
(arrows)
drawn
around
a
positive charge shows the direction and strength of the force
that would be exerted on another + charge placed at any point in the
pattern. Would
the electric field at Point X below, halfway between a + and a - charge, point
toward the right, the left, or would the electric field be zero?
+
X
-
Electromagnetic radiation (15 pts).
The
most
important
of
the
4
energy
transport processes (why?).
Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that can propagate (at the
speed of light) through empty space (and also transparent materials
like glass & air). Radiation
can be produced by
moving charges. You add energy to cause the charges to oscillate and
produce the radiation. Energy reappears when the resulting radiation
causes electrical charges somewhere else to move. Wavelength is one way
of distinguishing between different types of radiation (frequency is
another). Would a slowly-oscillating charge produce long- or
short-wavelength radiation? Would this be a relatively high- or
low-energy form of radiation? Electromagnetic spectrum. We will mostly
be concerned with ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS), infrared (IR) light.
What is the wavelength interval for visible light? What is white light?
Does red light have longer, shorter, or the same wavelength as blue
light? Wavelength units.
Rules governing the
emission of
radiation (10 pts). What
determines how much and what type of radiation an object will emit
(the same variable is found in both the Stefan-Boltzmann law
and Wien's
law)? A light bulb connected to a dimmer switch was used to
demonstrate. Radiant energy emitted by the earth (300 K) and sun (6000
K).
Sample Questions
Quiz
#2: 11, 12d&e, 13, 14, 15 Final
Exam: 15, 36
Radiative
equilibrium (5 pts).
Energy balance. Incoming radiant energy (sunlight) is balanced
by an
equal amount of (but not necessarily the same kind of) outgoing radiant
energy, temperature remains constant.
Filtering
effect of the atmosphere (10 pts).
Does the atmosphere mostly absorb, selectively absorb, or mostly
transmit UV, VIS, and IR radiation? What gases are important in each
case? What does the term window mean? What property makes water vapor,
carbon dioxide, methane, etc. greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse
effect
(simplified
view)
(15 pts).
With an atmosphere (containing greenhouse
gases), the
temperature of the earth's surface is warmer than it would be without
an atmosphere. H2O, CO2, and other greenhouse
gases selectively absorb
IR radiation. The atmosphere in turn radiates IR radiation into space
and back toward the ground. How is it possible for the earth's surface
to radiate away more energy than it receives from the sun and still be
in energy balance? What effects do clouds have on
nighttime and daytime
temperatures? Why?
Earth-atmosphere
energy
budget
(10 pts).
Two relatively easy questions:
(i) What percentage of the
sunlight arriving at the top of the atmosphere reaches the ground and
is absorbed? (ii) What happens to the remaining sunlight? These
next questions are a little harder: (i) Why does the
atmosphere emit more energy downward toward the ground than upward into
space? (ii) How is it possible for the earth's surface to emit
more radiant energy than it gets from the sun? (iii) On average
does the earth's surface get more radiant
energy from
the
sun or from the atmosphere?
Sample Questions
Quiz #2: 2, 7, 8, 12a,b,&c,
EC3 Final Exam:
20 See also this 2nd set of Sample
Questions
Controls of
temperature (15 pts).
You should understand how latitude, proximity to land or ocean,
and
altitude affect the annual average temperature and the annual range of
temperature at a particular location. Where are the hottest and
coldest locations on earth?
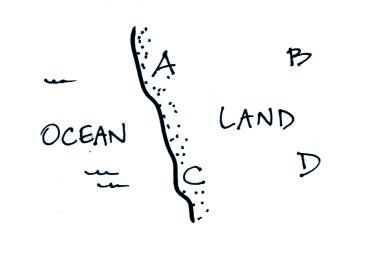
Which city in the figure above at
left (all found at the same
altitude)
would have the hottest summertime temperatures? Which city would
have the coldest wintertime temperatures? Which city would have
the largest annual range of temperature? Which city would have
the smallest annual range of temperature?
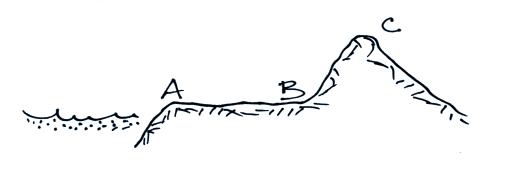
All three cities in the figure above at right are located at the
same
latitude. Which city would have the smallest annual temperature
range? Which city would have the lowest annual average
temperature?
Which city would be hottest in the summer? Which city would be
coldest
in the winter?
Sample
Questions:
Quiz #3:
1, 10 Final: 29
Causes of the Seasons (15 pts) Earth's orbit around the
sun. When is the earth closest to and furthest
from the sun? What is the earth's orientation, relative to the plane of
its orbit
around the sun, on the solstices and equinoxes? When do the solstices
and equinoxes occur? The changing orientation of the earth means that
the angle at which sunlight strikes the ground will vary during the
year. Is more energy delivered to the ground when the sun is high or
low in the sky? Why (there are a couple of reasons)? What is the other
factor that determines how much energy arrives at the ground during the
day?
Sample
Questions
Reviews
Mon., Mar. 7
|
2-3 pm
4-5 pm
|
SocSci 222
SocSci 222
|
Tue., Mar. 8
|
4-5 pm
|
FCS 225
|